Guinea Pig vs. Hamster: Which Pet Is Right for You?
Compare care and temperaments to discover which small companion fits your lifestyle.
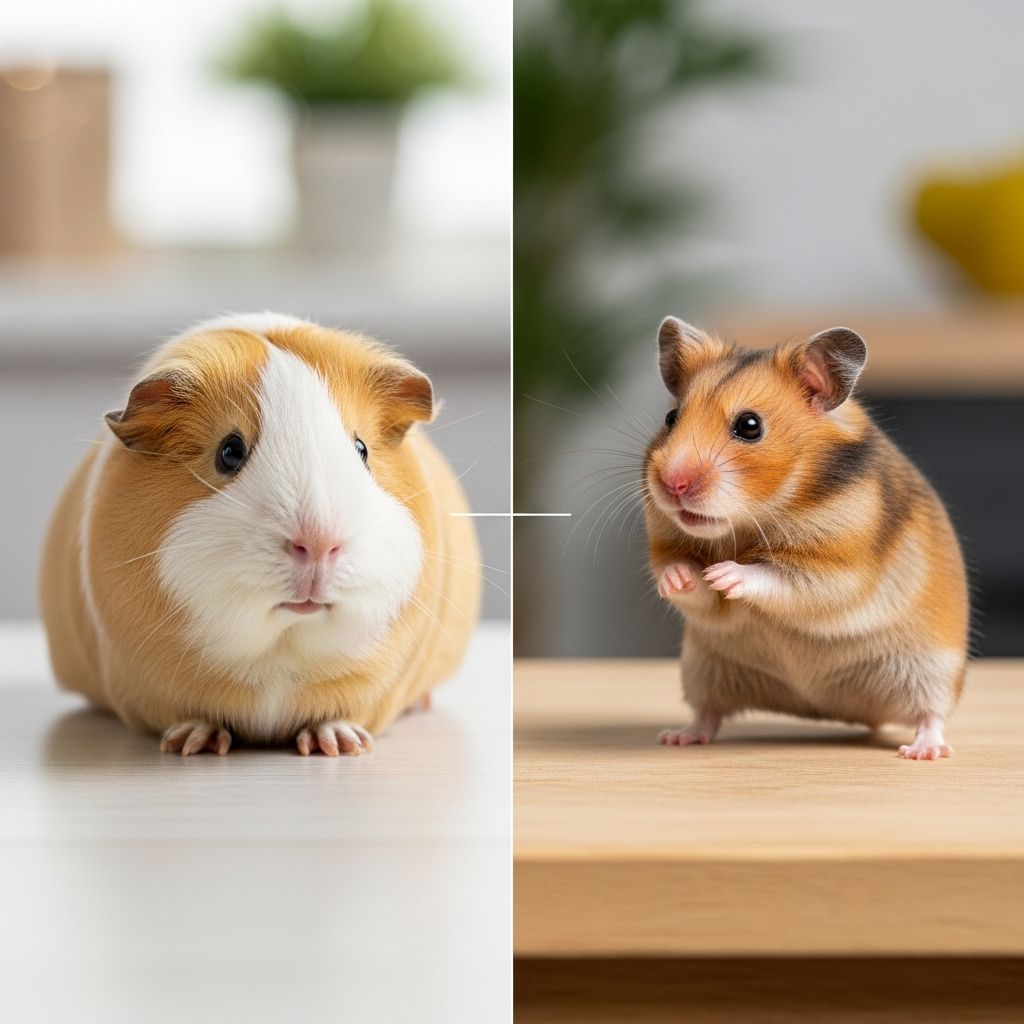
Guinea Pig vs. Hamster: Which Small Pet Is Right for You?
Choosing a new small animal companion can be exciting but overwhelming. Among the most popular pocket pets, guinea pigs and hamsters seem similar at first glance. However, they’re actually quite different—each with unique traits, care requirements, and personalities. This in-depth guide explores every aspect of the guinea pig vs. hamster debate to help you find the best fit for your home, lifestyle, and expectations.
Table of Contents
- Origins and Species Differences
- Size and Appearance
- Lifespan
- Diet and Feeding
- Personality and Behavior
- Housing and Space Needs
- Sleeping Patterns and Activity
- General Care and Maintenance
- Cost of Care
- Common Health Issues & Veterinary Care
- How to Decide: Which is Right for You?
- Frequently Asked Questions
Origins and Species Differences
Guinea pigs and hamsters are both rodents, but they come from different branches of the rodent family tree and have distinctly different backgrounds:
- Guinea Pigs: Native to the mountains of South America (Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, and Bolivia), guinea pigs belong to the genus Cavia. Thousands of years ago, they were domesticated by indigenous cultures. Today’s pet guinea pigs are gentle companions far removed from their wild ancestors.
- Hamsters: Hamsters are a group of about 25 species in the Cricetinae subfamily. The most common pet hamsters are Syrian (golden) hamsters and several species of dwarf hamsters. Their natural habitats range across Europe and Asia, from plains to deserts.
Fun fact: Guinea pigs are not “pigs” and have nothing to do with Guinea. The name is a historic misnomer.
Size and Appearance
One of the most obvious differences between guinea pigs and hamsters is their physical size and overall look.
| Guinea Pig | Hamster | |
|---|---|---|
| Weight | 1.5–2.6 pounds (700–1200 grams) | 1–10 ounces (28–280 grams) |
| Length | 8–12.5 inches (20–32 cm) | 2–6 inches (5–15 cm) |
| Body Shape | Plump, stocky, rounded, short neck, no visible tail | More “rodent-like” with visible short tail (esp. smaller breeds), more pronounced face |
| Young | Born fully furred, eyes open | Born hairless and blind |
| Other features | Large round head, stumpy neck, wide variety of coat colors and patterns | Compact bodies, can have either short or long fur, various colors and markings |
Guinea pigs are visibly much larger and need correspondingly more space than hamsters.
Lifespan
Guinea pigs live significantly longer than hamsters:
- Guinea Pig: 5–8 years (some live up to 10 years with excellent care)
- Hamster: 2–3 years (rarely up to 4 years)
If you’re seeking a longer-term companion, guinea pigs offer more years, but this also means a greater commitment in the long run.
Diet and Feeding
| Guinea Pig | Hamster | |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Strict herbivore (plant eater) | Omnivore (plant and animal matter; e.g., seeds, grains, insects) |
| Staple Foods | Hay, fresh vegetables, vitamin C-rich foods, guinea pig pellets | Seeds, grains, fresh fruit/veg, occasional protein source like mealworms |
| Special Considerations | Requires constant access to hay for digestive health and dental wear; cannot synthesize vitamin C (supplement needed) | Needs food variety and occasional treats for enrichment |
Guinea pigs must never eat meat, whereas hamsters may occasionally eat small insects as part of their diet. Both require fresh water at all times.
Personality and Behavior
Their personalities are as different as their appearances:
- Guinea Pigs: Highly social, gentle, and interactive. They thrive in pairs or groups, love human attention, and communicate with a variety of cheerful squeaks, chirps, and purrs. Generally not aggressive and rarely bite unless scared.
- Hamsters: Solitary by nature (especially Syrian hamsters; dwarf species may tolerate each other). More independent, may be skittish or nippy without regular gentle handling. Active and curious but generally prefer observing over cuddling. Susceptible to stress when housed together with other hamsters.
Hamsters are more likely to entertain themselves, while guinea pigs may demand more time and engagement from their owners.
Housing and Space Needs
Guinea pigs and hamsters both need safe, stimulating habitats, but their space requirements are quite different.
- Guinea Pig: Requires much larger living quarters—a spacious cage or enclosure with minimum 7.5 square feet for one or two piggies, larger for groups. They need flat, solid flooring and plenty of room to run, hide, and explore.
- Hamster: Suited to smaller cages or modular habitats due to their petite size. They enjoy tunnels, wheels, and levels for climbing, but wire floors must be avoided to prevent foot injuries.
Both require regular bedding changes, hiding places, and safe chew toys. Hamsters favor deeper bedding for burrowing, while guinea pigs enjoy tunnels and open floor space.
Sleeping Patterns and Activity
| Guinea Pig | Hamster | |
|---|---|---|
| Activity Pattern | Crepuscular (active at dawn and dusk, plus throughout day) | Nocturnal (active at night; sleeps during the day) |
| Suitability for Children | Easier to interact with during the daytime | Mostly sleeps when kids are home; active (and sometimes noisy) at night |
Guinea pigs are present and interactive for much of the day, fitting more naturally into a typical family’s schedule. Hamsters’ nighttime activity means they’re best suited to night owls or quieter households.
General Care and Maintenance
- Guinea pigs require more time-consuming daily care: feeding, cage cleaning, social interaction. Their enclosures must be kept clean and dry to prevent respiratory and skin problems.
- Hamsters are often considered “lower maintenance” due to their independence and smaller size, but they are not “automatic” pets. Cages should be cleaned regularly, and enrichment opportunities are essential to prevent boredom.
Both deserve careful attention to their environment. Guinea pigs especially should have their bedding changed more often due to their size and group living, while hamsters’ cages can develop odor if not cleaned regularly.
Cost of Care
While both make affordable pets compared to dogs or cats, there are differences in ongoing costs:
- Guinea pigs: Higher initial cage and accessory costs, more food (esp. fresh veggies and hay), and more bedding over time due to longer life spans and size.
- Hamsters: Lower set-up and maintenance costs, smaller quantities of food and bedding; however, they still require periodic investment in toys, proper nutrition, and veterinary care.
Neither pet should be considered “cheap”—both deserve quality care, balanced diets, and regular vet visits. Guinea pigs’ longer lives may mean a higher total investment.
Common Health Issues & Veterinary Care
- Guinea Pigs: Prone to dental disease (because their teeth grow continuously), vitamin C deficiency (scurvy), respiratory infections, and sometimes skin issues. Require more frequent veterinary checkups due to these health vulnerabilities.
- Hamsters: Can suffer from wet tail (a serious intestinal disease), cheek pouch impactions, respiratory illnesses, and trauma from falls or cage injuries. Hamsters tend to be resilient but need prompt attention if illness is suspected.
Both species benefit from vets who specialize in small mammals or exotics. Preventative care, clean environments, and correct nutrition are essential for both hamsters and guinea pigs.
How to Decide: Which is Right for You?
Ultimately, your choice between a guinea pig and a hamster should reflect:
- Your lifestyle and time commitment
- Space available in your home
- The ages and schedules of household members (especially children)
- Your desire for social interaction & handling
- Commitment to long-term care
Here’s a quick summary table to help you decide:
| Factor | Guinea Pig | Hamster |
|---|---|---|
| Lifespan | 5–8 years | 2–3 years |
| Size | Large | Small |
| Personality | Social, prefers company | Solitary, independent |
| Care | Higher; daily social needs | Lower; more independent |
| Housing | Spacious enclosure | Compact habitat |
| Ideal for | Families, those wanting interactive pets | Individuals seeking independent pets |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Are guinea pigs easier to take care of than hamsters?
A: Not necessarily—guinea pigs are generally considered more demanding, since they require larger habitats, frequent social interaction, and more fresh food prep. Hamsters need less space and are more independent, but both require regular cleaning and enrichment.
Q: Can guinea pigs and hamsters live together in the same cage?
A: No. Hamsters and guinea pigs have different social needs, dietary requirements, and risk injuring each other. They should never be housed together.
Q: Are guinea pigs or hamsters better for kids?
A: Guinea pigs are usually a better fit for young children because they’re awake during the day and gentle when handled properly. Hamsters, being nocturnal and sometimes nippy, may not suit younger kids.
Q: Which pet is more social: guinea pigs or hamsters?
A: Guinea pigs are much more social and should be kept in pairs or groups. Hamsters tend to be solitary—especially Syrian hamsters—and may fight if kept together.
Q: Can hamsters or guinea pigs bite?
A: Any animal may bite if frightened. Hamsters are more likely to nip, especially if startled. Guinea pigs rarely bite if handled gently and correctly.
Q: Which pet lives longer?
A: Guinea pigs typically live 5–8 years or more, while hamsters live about 2–3 years.
Final Thoughts
Both guinea pigs and hamsters can make charming, rewarding pets, but their needs and natures are very different. Guinea pigs are best for families ready for a longer commitment and who want an interactive, social animal. Hamsters are a better choice for those who have less space, are seeking a solo pet, or prefer a more hands-off companion. Consider your lifestyle, expectations, and the commitment you can provide before welcoming any new pet into your family.
References
- https://haypigs.com/en-us/blogs/haypigs/2019-3-14-what-is-the-difference-between-a-hamster-and-a-guinea-pig
- https://www.coopsandcages.com.au/blog/guinea-pig-vs-hamster/
- https://www.chewy.com/education/small-pet/hamster/hamster-vs-guinea-pig
- https://kavee.com/blogs/the-piggy-blog/hamsters-vs-guinea-pigs
- https://blog.omlet.us/2021/09/07/whats-the-difference-between-a-hamster-and-a-guinea-pig/
Read full bio of Srija Burman












