Whiteheads on the Lip Line: Comprehensive Guide to Causes and Targeted Treatment Strategies
Combine simple home routines with expert advice to clear stubborn spots around your mouth.
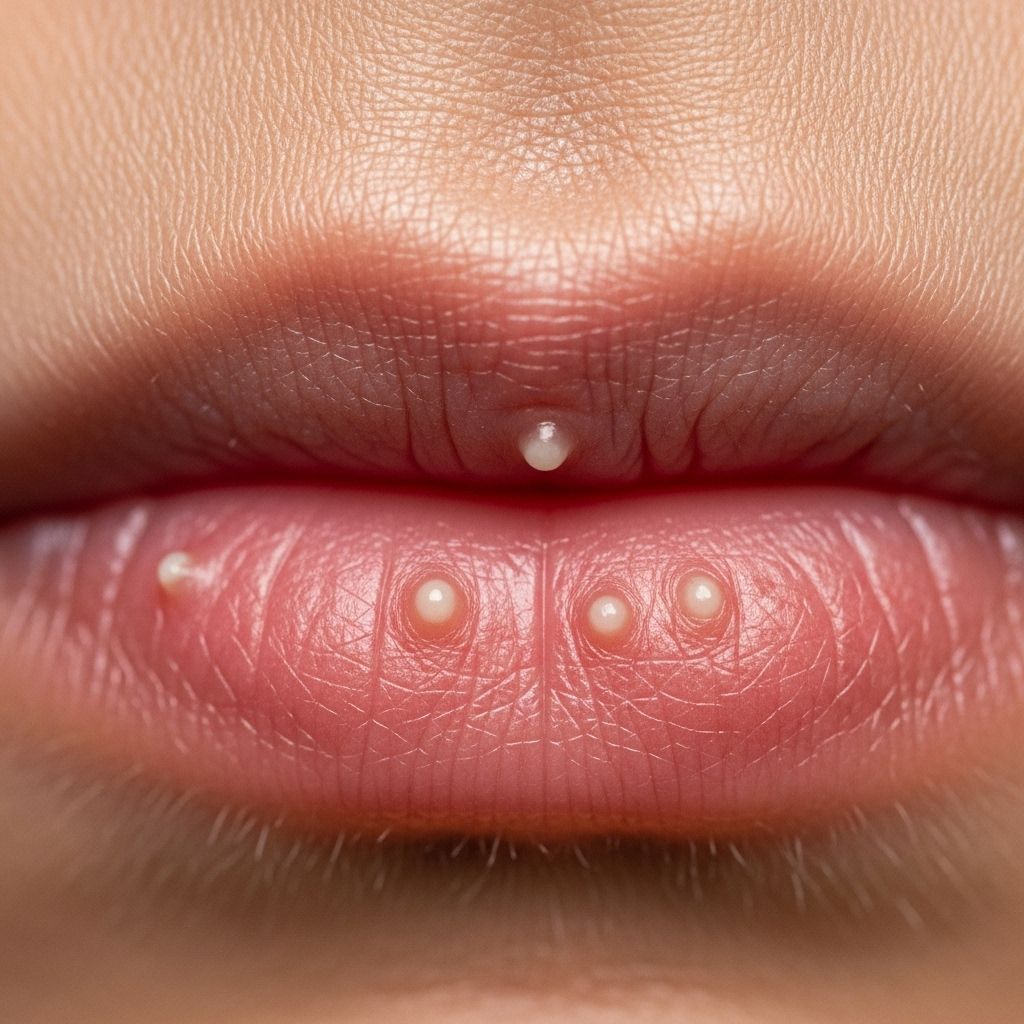
Whiteheads on the Lip Line: Causes & Targeted Treatment
The appearance of whiteheads on the lip line can be distressing and uncomfortable, especially considering the sensitivity and aesthetic importance of the lips. While often benign, these white bumps can sometimes signal underlying skin or health issues. Understanding the root causes, distinguishing between various types, and knowing which treatments are both safe and effective is essential for maintaining optimal lip health and appearance.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Whiteheads on the Lip Line
- Common Causes of Whiteheads on the Lip Line
- Whiteheads Vs. Milia, Fordyce Spots, and Cold Sores
- Risk Factors and Triggers
- Targeted Treatment and Home Care Solutions
- Prevention Strategies
- When to See a Dermatologist
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Understanding Whiteheads on the Lip Line
Whiteheads are a form of acne characterized by closed comedones—small, white bumps caused by clogged hair follicles filled with oil, dead skin cells, and bacteria. While most commonly found on the face or forehead, it is not unusual to find them on or near the lip line. Due to the delicate skin in this area and the high concentration of sebaceous (oil) glands, whiteheads on the lips are particularly noticeable and sometimes uncomfortable due to frequent lip movement.
Common Causes of Whiteheads on the Lip Line
Identifying the underlying reason for a white bump near or on the lips is crucial for determining the correct treatment approach. The causes of whiteheads and similar bumps on the lip line include:
- Clogged Pores and Acne: The most common cause of whiteheads is trapped oil and debris within hair follicles, especially in areas rich in sebaceous glands like the lips.
- Milia: Small, hard, white bumps formed when keratin (a skin protein) becomes trapped under the skin. While more common on the face, milia can develop on the lips.
- Fordyce Spots: Benign, visible sebaceous glands that present as tiny, pale or white bumps on the inner lips. Completely harmless but sometimes mistaken for whiteheads.
- Herpes Simplex Virus (Cold Sores): While not true whiteheads, HSV outbreaks can appear as clusters of white or clear blisters on or near the lips. These are typically painful and often recur.
- Contact Dermatitis: Allergic reactions to certain products (lip balms, toothpaste, cosmetics) may trigger bumps including whiteheads.
- Oral Thrush: A fungal infection leading to white patches or bumps inside the mouth and occasionally on the lip border.
- Irritation from Hair Removal: Waxing or shaving the upper lip can cause trauma leading to blocked pores or folliculitis (inflammation of hair follicles) that appears as white bumps.
A Detailed Look at the Most Common Types
| Type | Appearance | Location | Symptom | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Whitehead (Acne) | Small, white-tipped bump | Lip line, corners, nearby skin | Mildly tender, possible redness | Benign, treatable at home |
| Milia | Tiny, hard white bumps (not inflamed) | Face, lips, eyelids | No pain or itching | Harmless, self-resolving |
| Fordyce Spots | Clusters, pale or white, 1-2 mm spots | Inner lip, lip border | None (asymptomatic) | Cosmetic only; no treatment needed |
| Cold Sores (HSV) | Grouped blisters, often clear or whitish | Lip line, mouth corners | Pain, tingling, swelling | Viral, requires different approach |
Whiteheads vs. Milia, Fordyce Spots, and Cold Sores
Distinguishing between these conditions is essential, not only for effective treatment but also for understanding which are harmless and which require medical attention:
- Whiteheads: Caused by clogged follicles; treatable with acne therapies; may be red or tender.
- Milia: Formed by trapped keratin; hard and painless; often resolve spontaneously or with topical retinoids.
- Fordyce Spots: Enlarged oil glands; uniform size; do not require removal but can be treated for cosmetic reasons.
- Cold Sores: Viral in origin; accompanied by pain, tingling, or itching; need antiviral treatment.
If a white bump is spreading, persistent, or associated with pain, ulceration, or any color changes, assessment by a medical professional is strongly recommended.
Risk Factors and Triggers
Certain factors can increase the risk of developing whiteheads or similar bumps along the lip line:
- Excessive production of oil (sebum) by sebaceous glands
- Poor facial hygiene practices or excessive use of harsh cleansers
- Use of oily or comedogenic lip balms and cosmetics
- Frequent lip touching, picking, or squeezing
- Hormonal changes (adolescence, menstruation, pregnancy)
- Diet high in sugars and processed foods
- Skin irritation (from shaving, waxing, or dental products)
- Underlying skin conditions or weakened immune system
Targeted Treatment and Home Care Solutions
Treatment strategies vary depending on the underlying cause; however, there are several safe and effective options for managing and removing whiteheads specifically on the lip line.
Lip Line Acne (Comedonal Whiteheads)
- Gentle Cleansing: Use a mild, non-comedogenic cleanser to remove excess oil and dirt twice daily. Avoid scrubbing, which can irritate skin further.
- Warm Compress: Applying a warm, damp cloth to the affected area for 5–10 minutes helps to open pores and promote healing, especially for whiteheads with visible pus heads.
- Spot Treatments: Over-the-counter products containing benzoyl peroxide or salicylic acid are helpful for targeting acne-causing bacteria and unclogging pores.
- Hands Off: Avoid picking, squeezing, or touching the bumps to minimize risk of further infection and scarring.
- Keep Lips Clean: Regularly remove makeup and lip products at the end of the day.
- Medicated Lip Care: Apply balms or treatments specifically designed for acne-prone skin, avoiding heavy or greasy formulas.
- Prescription Medication: For persistent or severe cases, a dermatologist may prescribe topical or oral retinoids or antibiotics.
Milia Removal Techniques
- Do not attempt to extract milia at home; improper removal can lead to skin damage or infection.
- Dermatologists may use sterile extraction, topical retinoids, chemical peels, cryotherapy, or gentle laser procedures for stubborn cases.
Managing Fordyce Spots
- Because they are harmless, Fordyce spots do not require medical treatment unless for cosmetic reasons.
- Laser therapy, electro-surgery, or prescription retinoid creams are sometimes used for cosmetic removal under medical supervision.
Addressing Cold Sores and Oral Thrush
- Cold Sores: Treated with topical or oral antiviral medications (e.g., acyclovir); avoid triggers and maintain good immunity.
- Oral Thrush: Antifungal agents are required; seek medical advice if white patches extend inside the mouth.
Other Helpful Home Remedies
- Keep the area dry and clean: This minimizes bacterial and fungal growth.
- Castor Oil: Known for its anti-inflammatory properties, a dab of castor oil may help soothe the bump.
- Hot or Cold Compress: Alternating compresses may relieve swelling and discomfort.
Prevention Strategies
Long-term management and prevention of whiteheads on the lip line include:
- Choose Non-Comedogenic Products: Select lip balms, moisturizers, and makeup labeled “non-comedogenic” or “oil-free.”
- Maintain Facial Hygiene: Cleanse your face and lips gently but thoroughly every morning and night.
- Avoid Touching Lips Repeatedly: This prevents the spread of bacteria and minimizes irritation.
- Hydrate Well: Drink plenty of water to support skin health.
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Minimize intake of sugary, fatty, or processed foods which may exacerbate acne development.
- Replace Toothbrushes Regularly: Bacteria on toothbrushes or lip products can aggravate breakouts.
When to See a Dermatologist
Most white bumps on the lip line are benign and resolve with simple at-home care. However, schedule a visit with a dermatologist if you:
- Notice white bumps that persist for several weeks or increase in number
- See changes in color, texture, or develop pain, bleeding, or ulceration
- Experience frequent outbreaks or have underlying health conditions
- Face difficulty distinguishing between a simple whitehead and other lip lesions (such as cold sores or oral cancer)
Early professional evaluation may be required for ambiguous, painful, or rapidly changing lip lesions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: How can I tell if the white bump on my lip is a whitehead or a cold sore?
Whiteheads are usually hard, painless, and not accompanied by tingling or swelling. Cold sores often start with a tingling or burning sensation and appear as clusters of fluid-filled blisters, which break and crust over. Cold sores are also often painful and recur in the same area.
Q: Are whiteheads on the lip line contagious?
No. Whiteheads themselves are not contagious; however, cold sores (caused by HSV) are highly contagious.
Q: Can I pop a whitehead on my lip?
Do not pop whiteheads (or any other bumps) on your lip as this increases risk for infection, scarring, and delayed healing.
Q: How long do whiteheads on the lip line typically last?
Whiteheads can resolve in several days with proper care. Milia and Fordyce spots may persist much longer but usually don’t require intervention. Seek advice if bumps last more than two weeks or worsen.
Q: What if the white bump grows or changes color?
Consult a healthcare professional if you notice rapid growth, color or texture changes, bleeding, or ulceration, as this may suggest another underlying condition requiring medical assessment.
Key Takeaways
- Whiteheads on the lip line are typically caused by clogged pores, milia, or Fordyce spots, and are usually benign.
- Treatment involves gentle cleansing, non-comedogenic skin products, warm compresses, and avoiding picking or squeezing.
- Persistent, painful, or changing bumps merit a professional dermatological evaluation to rule out more serious conditions.
- Long-term prevention focuses on diligent skin hygiene, product choice, and minimizing skin irritation.
Ultimately, most cases of whiteheads and similar bumps along the lip line can be managed safely at home or with professional guidance without significant discomfort or cosmetic concern.
References
- https://www.healthline.com/health/white-bumps-on-lips
- https://health.osu.edu/health/skin-and-body/what-is-this-white-bump-on-my-lip
- https://www.riodentaltx.com/5-ways-to-deal-with-a-lip-pimple/
- https://health.clevelandclinic.org/pimple-on-lip
- https://www.healthline.com/health/how-to-get-rid-of-pimple-on-lip
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/how-to-get-rid-of-pimple-on-lip
- https://health.clevelandclinic.org/cold-sore-vs-pimple-on-lip
Read full bio of Sneha Tete












