Sensory Deprivation Tanks (Floating): Transforming Mental Health and Well-Being
Embrace sensory silence to soothe anxiety, sharpen focus, and spark creativity.
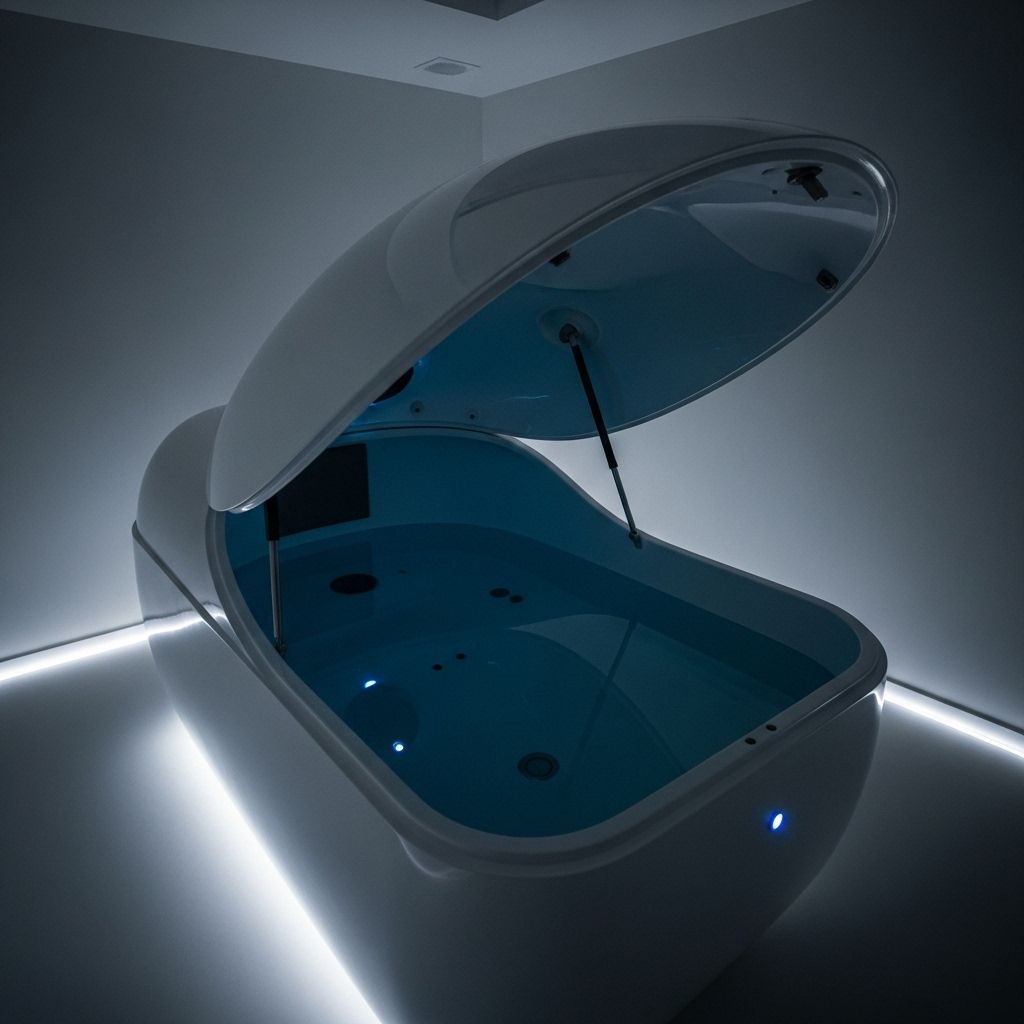
Sensory deprivation tanks, often called float tanks or isolation tanks, have surged in popularity as a holistic approach for supporting mental health, well-being, and relaxation. Immersing users in an environment devoid of external sensory input, these tanks offer a unique mental health intervention that is both ancient in concept and modern in application.
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Sensory Deprivation Tanks
- How Sensory Deprivation Tanks Work
- Therapeutic Benefits for Mental Health
- Physical Effects and Medical Applications
- Psychological and Cognitive Effects
- Creativity and Peak Performance
- What to Expect: The Sensory Experience
- Quality of Evidence and Limitations
- Potential Risks and Who Should Avoid Floating
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Conclusion
Introduction to Sensory Deprivation Tanks
Sensory deprivation tanks, also known as floatation tanks or isolation tanks, are lightproof, soundproof chambers filled with a shallow pool of warm water, heavily saturated with Epsom salt. By minimizing environmental stimuli, these tanks create a unique therapeutic environment that targets the mind and body for deep relaxation, introspection, and healing.
The concept of sensory deprivation was first developed in the mid-20th century by neuroscientist Dr. John C. Lilly, who sought to understand how the brain responded to a lack of external input. Today, float tanks are embraced by professionals, athletes, mental health practitioners, and individuals seeking relaxation, personal growth, or relief from various conditions.
How Sensory Deprivation Tanks Work
A typical float tank is filled with about 10-12 inches of water, heated to match the skin’s surface temperature (~35°C/95°F), and saturated with hundreds of kilograms of Epsom salt (magnesium sulfate) to ensure effortless buoyancy. Users float nude in silence and darkness, with all external stimuli (audio, visual, tactile) minimized. This absence of sensory input is referred to as restricted environmental stimulation therapy (REST).
- Buoyancy: The high salt content allows the body to float weightlessly, removing pressure from joints and muscles.
- Temperature: Water is kept at skin temperature, making it difficult to distinguish between body and environment.
- Isolation: The tank’s design prevents light and sound from entering, quieting the mind significantly.
Therapeutic Benefits for Mental Health
Research and anecdotal evidence indicate several mental health benefits from floating regularly in sensory deprivation tanks:
- Stress reduction: Users consistently report profound relaxation and reduced stress after sessions. The absence of external stimuli facilitates a deep state of calm, often compared to advanced meditation practices.
- Anxiety relief: Studies demonstrate significant decreases in both acute and chronic anxiety symptoms. One 2018 study showed a single one-hour session could reduce symptoms of anxiety and improve mood for individuals with stress- and anxiety-related disorders.
- Improved mood and emotional stability: Float sessions are linked to increased feelings of well-being, optimism, and even mild euphoria. Some users report experiencing deep peace and spiritual insight.
- Reduction of depressive symptoms: Evidence points to floating as a promising adjunct intervention for mild to moderate depression.
- Sleep enhancement: Many practitioners observe better sleep, with reductions in insomnia and fatigue following regular floating.
Scientific Highlights
- A 2016 study found that individuals with generalized anxiety disorder not only experienced reduced anxiety but also improvements in depressive symptoms, sleep difficulties, irritability, and fatigue following float sessions.
- Repeated sessions further amplify these benefits, with most participants observing lasting changes after several weeks of regular practice.
Physical Effects and Medical Applications
While the mental health benefits of sensory deprivation tanks attract the most attention, there are also significant effects on the body:
- Muscle relaxation and pain relief: The weightless environment and high magnesium content help relieve muscle tension, joint pain, and chronic pain conditions (such as fibromyalgia or whiplash-associated disorders).
- Reduced inflammation: Epsom salt’s magnesium may decrease inflammation, improve circulation, and promote muscle and joint recovery.
- Improved cardiovascular health: Deep relaxation induced by flotation can reduce stress hormones (e.g., cortisol), blood pressure, and heart rate, benefiting cardiovascular well-being.
- Enhanced skin and hair health: Magnesium from the water acts as a skin exfoliant and may improve the health of hair and nails.
Psychological and Cognitive Effects
Sensory deprivation’s impact on the psyche is complex and profound, affecting both conscious awareness and subconscious processing.
- Hallucinations and altered states: Some users, particularly those prone to imaginative or dissociative experiences, report hallucinations or intense dreamlike imagery in the tank. Studies confirm that short-term sensory deprivation can induce such psychosis-like experiences, although they generally dissipate after exiting the tank.
- Mindfulness and meditative insight: The absence of sensory distraction can foster a deep meditative state, facilitating mindfulness, introspection, and emotional processing similar to advanced meditation or yoga nidra.
- Improved cognitions: Some research links regular floating to clearer thought, better focus, and enhanced ability to retain new information.
Creativity and Peak Performance
Floating is not just for those seeking relief from stress or illness; it is also a tool for personal development, creative enhancement, and professional optimization.
- Creativity: Multiple studies indicate floating can boost originality, imagination, and intuition—attributes known to enhance creative output. Users often report breakthroughs in problem-solving or new ideas during or after float sessions.
- Concentration and learning: The mental clarity following a float session supports improved focus and precision, making float therapy of interest to students and professionals.
- Athletic performance and recovery: Float sessions aid athletes by accelerating recovery after strenuous exercise, reducing muscle lactate, lowering stress, and improving psychological recovery post-competition.
| Effect | Mental Health | Physical Health | Cognitive/Performance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stress Relief | Yes | Yes (reduces stress hormones) | Improved focus |
| Anxiety Reduction | Yes | Sometimes (via muscle relaxation) | Enhanced emotional regulation |
| Pain Relief | Secondary | Yes (especially chronic) | – |
| Creativity Boost | Yes | – | Significant increase |
| Better Sleep | Strong effect | Facilitates relaxation | – |
| Athletic Recovery | Improved mood | Yes | Faster return to training |
What to Expect: The Sensory Experience
For many first-timers, floating in a sensory deprivation tank can feel both unfamiliar and deeply calming. Here is what to expect:
- Arrive at the float center and shower before entering the tank (to maintain water hygiene).
- Enter the tank nude (swimsuits may affect the sensory experience).
- Lay back and feel your body become buoyant and weightless.
- The tank is completely dark and silent; even gravity’s effects seem to vanish.
- Initial distractions and racing thoughts may give way to deep relaxation within 10–20 minutes.
- The session typically lasts 60–90 minutes. When finished, shower again to remove salt from your skin and hair.
- Post-float, most people feel a lingering sense of calm, heightened awareness, and occasionally, vivid mental clarity or inspiration.
Quality of Evidence and Limitations
While a growing body of research supports the therapeutic effects of sensory deprivation floatation therapy, limitations remain:
- Many studies feature small sample sizes, short follow-up periods, and lack large-scale randomized control trials.
- Placebo effects and self-reporting biases may influence outcomes, especially concerning creativity, mood, or subjective well-being.
- More high-quality research is required to firmly establish protocols, long-term effects, and the optimal population groups.
Despite these limitations, both clinical findings and experiential reports point to significant therapeutic potential, particularly for stress, anxiety, and chronic pain management.
Potential Risks and Who Should Avoid Floating
Float therapy is generally considered safe for most healthy adults, but certain groups should consult a healthcare professional before use:
- Claustrophobia: The enclosed, dark space may trigger anxiety in those with claustrophobic tendencies. Some centers offer open pools to minimize this risk.
- Epilepsy: Uncontrolled epilepsy may pose a risk; floating should be avoided unless cleared by a doctor.
- Acute skin conditions: Open wounds, skin infections, or severe psoriasis may be aggravated by the salt content.
- Pregnancy: While many pregnant people safely use float tanks (with medical approval), always check with your healthcare provider, especially for high-risk pregnancies.
- Other medical contraindications: Heart disease, severe mental illness, or substance intoxication are additional risk factors.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Do you hallucinate in a sensory deprivation tank?
Some users, especially those with creative or imaginative tendencies, do report hallucinations or vivid internal imagery during float sessions. While uncommon, it is generally safe and typically subsides once the session ends.
Q: Will I get claustrophobic in the float tank?
Most people do not feel claustrophobic, since the tank is large enough to allow free movement and some can be left open. Those with strong claustrophobic reactions may find open-room tanks more comfortable.
Q: How often should I float to see benefits?
Even one session can yield noticeable effects, especially around stress and anxiety. For long-lasting mental health benefits, weekly or bi-weekly sessions are recommended.
Q: What should I do if I fall asleep inside?
Falling asleep is safe—your body will continue to float and the staff monitors safety. Many users achieve deep relaxation akin to brief naps or light sleep.
Q: Is float therapy covered by insurance?
Currently, most insurance providers do not cover sensory deprivation or float therapy, as it is considered alternative or complementary medicine. Some flexible spending accounts (FSAs) might apply if recommended for pain or stress management—check with your provider.
Q: Can children use float tanks?
Float therapy is usually restricted to older teens and adults. Some centers may allow children under supervision, but always consult medical professionals first.
Conclusion
Sensory deprivation tanks serve as powerful tools for unlocking deep physical relaxation, emotional healing, and enhanced cognitive performance. Supported by a growing, though still emerging, scientific foundation, floatation therapy promises accessible and profound pathways for stress relief, anxiety management, pain reduction, and creative discovery. As research continues, sensory deprivation tanks may become an increasingly mainstream pillar of both mental and physical well-being.
References
- https://www.healthline.com/health/sensory-deprivation-tank
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/sensory-deprivation-tank-benefits
- https://orwfoundation.org/floatation-therapy/
- https://health.clevelandclinic.org/float-therapy-benefits
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4219027/
- https://truerest.com/float-therapy-benefits-zero-gravity-and-sensory-deprivation/
- https://saltmb.com/blog/5-float-therapy-benefits-for-mental-and-emotional-health
Read full bio of Sneha Tete












