Ceramides & Niacinamide: Powerful Allies for Skin Barrier Repair, Hydration, and Resilience
Dual-action care that fortifies the skin barrier while delivering lasting hydration.
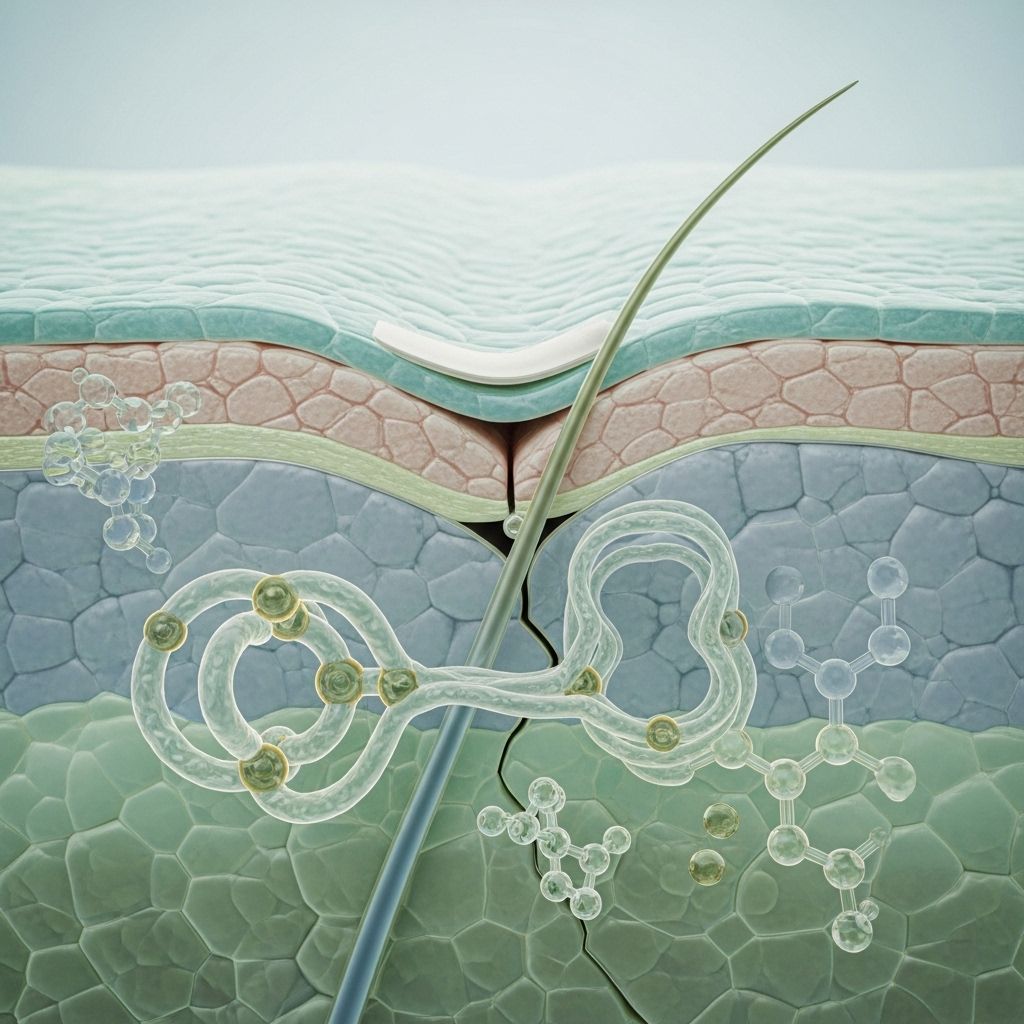
Ceramides & Niacinamide: Repairing Skin Barrier
The skin barrier is your body’s frontline defense—an intelligent wall of cells and lipids acting as a gatekeeper against moisture loss, environmental stressors, and pathogens. Two ingredients have emerged as leaders in restoring and enhancing this barrier: ceramides and niacinamide. Extensive clinical research and dermatological practice affirm their joint effectiveness in repairing, strengthening, and maintaining skin health, making them essential components of modern skincare routines.
Table of Contents
- Understanding the Skin Barrier
- What Are Ceramides?
- Benefits of Ceramides for Skin
- What is Niacinamide?
- Benefits of Niacinamide for Skin
- The Synergistic Power of Ceramides & Niacinamide
- Recognizing Skin Barrier Damage & Repair Strategies
- Choosing and Using Skin Barrier Repair Products
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- References
Understanding the Skin Barrier
The skin’s outermost layer, known as the stratum corneum, comprises tightly packed cells (corneocytes) embedded in a matrix of lipids. This complex structure is pivotal in:
- Retaining moisture within the skin
- Blocking entry of irritants, allergens, and microbes
- Protecting against mechanical, chemical, and UV damage
Lipid components—particularly ceramides, cholesterol, and fatty acids—form the ‘mortar’ between skin cells, ensuring barrier integrity. When these lipids are depleted, the barrier falters, contributing to dryness, irritation, redness, sensitivity, and flare-ups of skin conditions like eczema and rosacea.
What Are Ceramides?
Ceramides are naturally occurring lipids (fats) making up approximately 50% of the skin’s lipid matrix. They are essential for maintaining the cell cohesion essential for a healthy, functional barrier.
- Ceramides are ‘skin-identical’: structurally similar to those produced by your body.
- They act as the water-retaining mortar between skin cells.
- External factors (harsh cleansers, environmental stress, aging, UV exposure) can reduce ceramide levels.
This depletion triggers ‘barrier burnout’, microscopic cracks, increased ‘transepidermal water loss’ (TEWL), and vulnerability to irritants.
Benefits of Ceramides for Skin
- Immediate and long-term hydration: They lock in moisture and prevent dehydration.
- Repair of compromised barriers: Ceramide-based creams rapidly patch up microcracks and reinforce the lipid matrix.
- Protection against irritants: By restoring barrier function, ceramides defend against allergens, pollutants, and bacteria.
- Reduced sensitivity and inflammation: Supplementing ceramides calms redness, irritation, and reactivity, beneficial for eczema, psoriasis, and rosacea sufferers.
- Improved texture and resilience: Skin appears plumper, smoother, and more radiant with consistent ceramide use.
Chemists favor specific ratios for optimal barrier restoration. For acute repair, the 3:1:1 blend of ceramides, cholesterol, and fatty acids is highly effective; for maintenance and glow, a cholesterol-heavier 2:4:2 ratio is often used.
What is Niacinamide?
Niacinamide (vitamin B3) is a water-soluble vitamin praised for its multifunctional benefits. It is not an exfoliant or retinoid but instead works by supporting skin’s natural processes at a cellular level.
- Stimulates ceramide synthesis within skin cells.
- Enhances the strength and flexibility of the skin barrier.
- Reduces inflammation and regulates oil production.
Niacinamide is suitable for virtually all skin types, including sensitive and acne-prone skin.
Benefits of Niacinamide for Skin
- Barrier support: Promotes ceramide production and fatty acid synthesis, vital for a robust barrier.
- Reduces inflammation: Calms irritated skin, easing redness, and supporting conditions like acne, dermatitis, and rosacea.
- Regulates oil production: Controls excess sebum, helpful for oily or combination skin.
- Improves skin texture and tone: Diminishes appearance of dark spots, hyperpigmentation, and fine lines.
- Enhances elasticity: Supports keratin protein interactions, maintaining firmness and flexibility.
- Protects against oxidative stress: Shields cells from pollution, UV, and toxins.
- Accelerates skin healing: Rebuilds healthy skin cells following UV or environmental damage.
Clinical Evidence Table: Benefits Comparison
| Benefit | Ceramides | Niacinamide |
|---|---|---|
| Barrier Repair | Directly replenishes lipid matrix | Stimulates synthesis of ceramides |
| Hydration | Locks in moisture | Reduces water loss |
| Inflammation Reduction | Calms redness, sensitivity | Reduces irritation and redness |
| Texture & Elasticity | Improves plumpness | Boosts collagen, enhances elasticity |
| Oil Regulation | No direct effect | Regulates sebum |
| Pigment Correction | No direct effect | Reduces dark spots |
The Synergistic Power of Ceramides & Niacinamide
When combined, ceramides and niacinamide deliver superior skin barrier support and restoration. Dermatologists favor pairing them for the following reasons:
- Niacinamide boosts ceramide production internally, while topical ceramides rapidly replenish depleted external stores.
- Together, they dramatically reduce visible signs of inflammation, redness, and sensitivity.
- They create an optimal environment for healing, hydration, and long-term barrier strength.
- Both ingredients are suitable for sensitive, acne-prone, dry, oily, and mature skin.
For maximal effect, layer a niacinamide serum before applying a ceramide-rich cream, sealing in both hydration and active repair.
Recognizing Skin Barrier Damage & Repair Strategies
Barrier damage may be caused by external stressors or overzealous skin care (peels, cleansers, exfoliants) and can present as:
- Persistent dryness and flakiness
- Sensitivity, stinging, or burning sensations
- Redness and visible irritation
- Breakouts, itching, or rough texture
Repair strategies recommended by dermatologists include:
- Immediate use of a lipid-rich cream (containing ceramides, cholesterol, and fatty acids) to patch micro-damage.
- Incorporation of niacinamide in serums or moisturizers to boost endogenous ceramide synthesis and reduce inflammation.
- Reduction of irritating products (retinoids, acids) until the barrier regains stability.
- Prioritizing gentle cleansing and regular moisturization.
Recovery can be accelerated by the 3:1:1 lipid blend, clinically shown to repair damage as effectively as many mid-potency steroid creams for dermatitis.
Choosing and Using Skin Barrier Repair Products
- Look for ingredients like “ceramide NP/NG/AP/EOP,” cholesterol, fatty acids, and niacinamide in your products.
- Ceramide concentrations and lipid ratios matter for advanced barrier repair.
- Apply niacinamide serum first, then seal with ceramide-rich cream.
- Ideal for all skin types, especially when the barrier is compromised.
- Daily use supports both acute and ongoing maintenance of barrier integrity.
Many brands (CeraVe, SkinCeuticals, The Ordinary) offer formulations specifically targeting skin barrier restoration, often in dermatologist-recommended ratios.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Can ceramides and niacinamide be used together?
Yes, combining both supports optimal skin barrier conditions. Niacinamide stimulates natural ceramide production and calms inflammation, while topical ceramides restore lost lipids and reinforce the moisture barrier.
Q: Is niacinamide suitable for sensitive or acne-prone skin?
Absolutely. Niacinamide regulates oil, calms redness, and reduces sensitivity, making it versatile for sensitive, oily, and acne-prone skin. It does not cause purging or stinging.
Q: How can I tell if my skin barrier is damaged?
Signs include increased dryness, irritation, sensitivity, redness, and slow healing. Persistent symptoms may benefit from dermatologist consultation.
Q: How often should I use ceramide and niacinamide products?
Daily use is optimal for prevention and ongoing maintenance. Ceramides are best applied last, sealing your routine, while niacinamide works well as a serum underneath.
Q: Can ceramides and niacinamide help manage eczema or rosacea?
Yes, both have demonstrated effectiveness in soothing and restoring barriers in conditions such as eczema, psoriasis, and rosacea.
References
- Clinical studies and dermatologist recommendations regarding ceramides and niacinamide in skin barrier restoration
- Evidence of synergy in managing dry, sensitive, and inflamed skin
References
- https://www.revivalabs.com/your-skin-barrier-is-begging-for-these-ingredients-you-didnt-even-know-it/
- https://www.healthline.com/health/beauty-skin-care/niacinamide
- https://naturium.com/blogs/ingredient-library-blog/using-niacinamide-and-ceramides-together
- https://www.latimes.com/live-well/skin/story/ceramides-skin-barrier-repair
- https://www.orogoldcosmetics.com/ceramides-niacinamide-more-why-everyones-talking-about-barrier-repair/
- https://www.cerave.com.au/blog/everyday-skin-care/niacinamide-benefits-for-skin
- https://theordinary.com/en-us/blog/what-is-the-skin-barrier.html
- https://www.harpersbazaar.com/uk/beauty/skincare/a63454574/ceramides/
- https://www.dotandkey.com/blogs/skin-care/ceramide-moisturizers-skin-barrier-benefits
Read full bio of medha deb












