Blackheads on Ears: Causes, Prevention, and Safe Removal Techniques for Clearer Skin
Gentle routines that protect curves and ensure pores stay clear and irritation-free.
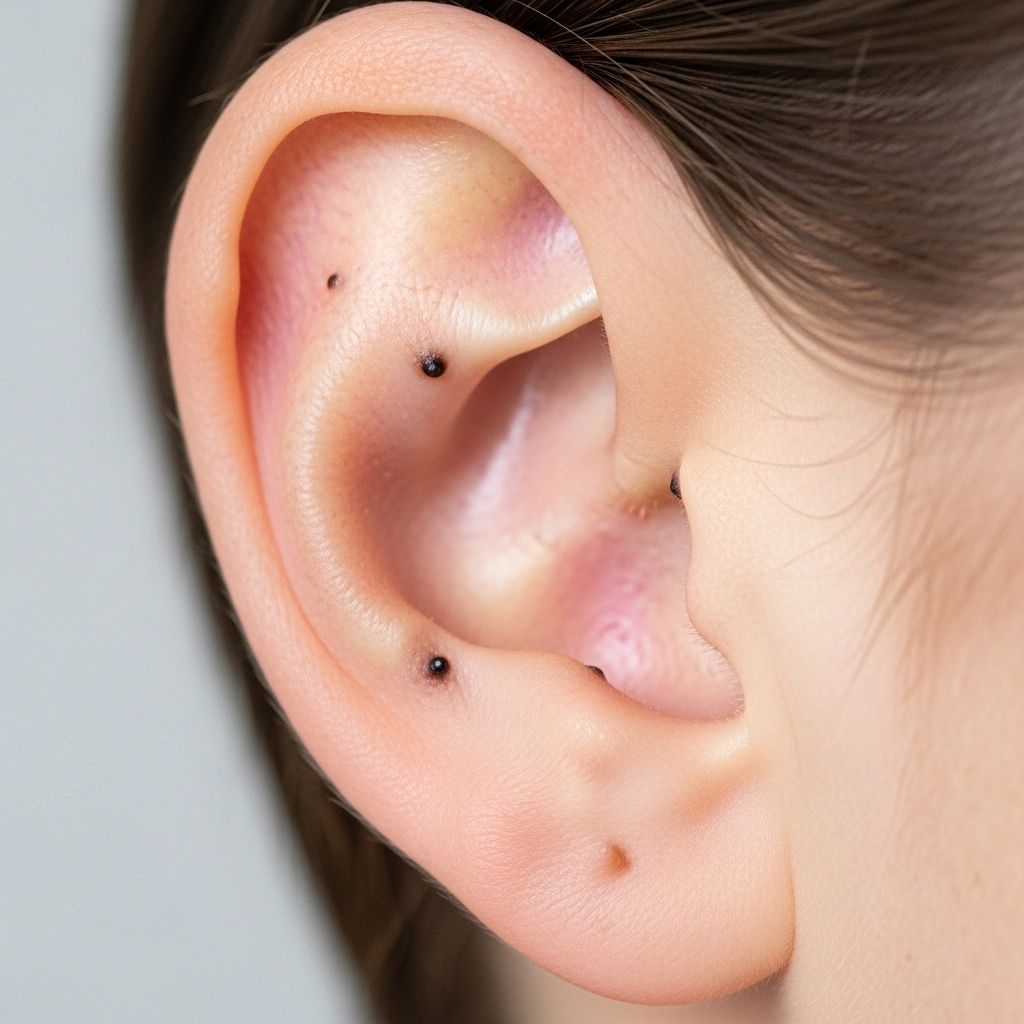
Blackheads are a common skin concern and while most people associate them with the nose or chin, they can also develop on and inside the ears. These tiny, stubborn spots not only mar the appearance but may cause discomfort if not addressed properly. This comprehensive guide explores the underlying causes of ear blackheads, effective prevention strategies, and expert-recommended, safe removal tips to help maintain healthy, clear skin around your ears.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Blackheads in Ears
- Primary Causes of Ear Blackheads
- Contributing Factors and Risk Groups
- Prevention Strategies
- Safe Removal Techniques
- When to Seek Professional Help
- Common Mistakes and Risks
- Home Care vs. Professional Treatment
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Conclusion
Understanding Blackheads in Ears
Blackheads are a type of non-inflammatory acne lesion, scientifically referred to as open comedones. They occur when dead skin cells, oil (sebum), and debris accumulate within a pore, creating a plug which, upon exposure to air, oxidizes and turns dark. While facial blackheads are well-known, the anatomy and physiology of the ear make it particularly vulnerable:
- Ear canal skin is covered in tiny hair follicles and glands.
- Sebaceous (oil) glands and ceruminous (earwax) glands both contribute to potential clogging.
- The ear’s structure can harbor bacteria, oils, and grime, increasing risk.
Blackheads in the ear can develop on both the outer ear (auricle, concha) and the entrance to the ear canal, but not deep inside, since sensitive middle and inner ear structures are protected.
Primary Causes of Ear Blackheads
A variety of biological and environmental factors contribute to the formation of blackheads in the ears:
- Excess Oil Production: An overactive sebaceous gland produces more oil, which mixes with dead skin cells and gets trapped in pores.
- Dead Skin Cell Build-Up: Poor skin turnover leads to accumulation of keratin and debris, compounding pore blockage.
- Bacterial Colonization: Bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus thrive in blocked pores, escalating risk for blackheads and eventual inflammation.
- Poor Hygiene: Infrequent cleaning or incomplete rinsing of the ear leads to dirt, sweat, and product residue build-up.
- Residual Hair Products: Shampoos, gels, and conditioners may not be rinsed out completely, leaving pore-clogging residues.
- Hormonal Changes: Fluctuations, especially during puberty, menstrual cycles, or medication changes (e.g., birth control pills), spur increased oil production.
- Environmental Exposure: Regular contact with dirty earbuds, headphones, pillowcases, cell phones, or hats increases infection and clogging risk.
Key Differences: Blackheads vs. Other Ear Acne
| Acne Type | Appearance | Primary Causes | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Blackhead (Open Comedone) | Flat, dark spot | Oil, dead skin, oxidized plug | Cleansing and chemical exfolients |
| Whitehead (Closed Comedone) | Small, white bump | Trapped oil and skin, covered plug | Gentle cleansing, topical solutions |
| Inflammatory Acne | Red, tender pimples | Bacteria, blocked pore, immune response | Topical antibiotics, avoid squeezing |
Contributing Factors and Risk Groups
Certain people and lifestyle habits are more prone to developing ear blackheads:
- Adolescents and Young Adults: Due to more active sebaceous glands.
- Individuals Using Oily or Heavy Hair Products:
- People Living in Humid or Polluted Environments:
- Those Frequently Using Earbuds, Headphones, Hearing Aids:
- Patients on Hormonal or Steroid Medications:
- Poor Hygiene Habits:
Conditions like hormonal imbalances, frequent sweating, or workplace exposure to dust and oils can increase susceptibility to ear blackheads.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing ear blackheads revolves around minimizing pore blockage and bacterial growth. The following strategies are dermatologist-recommended:
- Daily Cleansing: Gently clean the outside of the ears once or twice daily with a mild, non-comedogenic cleanser.
- Chemical Exfoliation: Use a salicylic acid (BHA) or glycolic acid (AHA) toner to loosen clogged pores; these ingredients dissolve oil and dead skin with minimal skin abrasion.
- Witch Hazel: A natural astringent that cleanses and disinfects skin, shrinking pores and reducing oil build-up.
- Regular Sanitization: Clean objects that contact your ears (earbuds, phones, pillowcases, hats) every few days to avoid bacterial transfer.
- Thorough Rinsing: Ensure no shampoo, conditioner, or styling product residue remains on or around ears when washing hair.
- Avoid Touching or Picking: Refrain from touching, squeezing, or picking blackheads to prevent infection, inflammation, or permanent scarring.
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Maintain a well-balanced diet, manage stress levels, and consider reducing heavy product use where possible.
- Monitor Medication Effects: Be aware of symptoms if on hormonal or steroid medications; consult your doctor if new skin issues arise.
Sample Preventive Routine
- Morning: Clean outer ear with gentle cleanser, rinse thoroughly.
- Twice weekly: Apply a BHA toner or mask around the outer ear (not inside the canal).
- Weekly: Disinfect earbuds, mobile phone, and pillowcase.
- After exercise or exposure: Wipe ears clean to remove sweat and oils.
Safe Removal Techniques
For safe blackhead removal, patience and gentle methods prevent complications. Experts advise the following steps:
- Start with Clean Hands and Tools: Always wash hands and sanitize tools (if used), such as cotton swabs or soft washcloths.
- Warm Compress: Apply a warm, damp cloth against the ear for several minutes; this helps soften the plug and open pores for easier cleaning.
- Gentle Cleansing: Use a mild cleanser or salicylic acid treatment to dissolve oil and debris. Apply around the blackhead, avoiding the ear canal.
- Topical Treatments: Apply a BHA- or AHA-based product (mask, toner) specifically formulated for acne-prone skin, targeting the area directly.
- Non-invasive Extractions: If the blackhead is prominent and on the outer ear, a gentle blackhead extractor tool may be used only by trained dermatologists. Home extractions risk trauma and infection.
- Moisturize: Apply a lightweight, non-comedogenic moisturizer to protect the skin after treatment.
Important: Never attempt extraction deep inside the ear or if the spot appears tender, inflamed, or infected. Squeezing or poking can lead to bleeding, infection, and permanent scarring.
When to Seek Professional Help
Certain scenarios require specialist intervention rather than home care:
- The blackhead is painful, swollen, or shows signs of infection (redness, heat, pus).
- Removal attempts cause bleeding or persistent tenderness.
- The blackheads persist or multiply despite routine care.
- Underlying skin conditions (such as discoid lupus) exhibit blackhead-like symptoms, but with associated scaling or other features.
- You suspect an allergic or adverse reaction to over-the-counter treatments.
Dermatologists may offer stronger prescription treatments, professional extraction, or lab analysis to rule out underlying skin diseases.
Common Mistakes and Risks
Avoid the following pitfalls for ear skin health:
- Popping and Picking: This can drive bacteria deeper, trigger inflammation, and cause permanent scarring.
- Using Sharp Objects: Never insert tweezers, pins, or unsterilized metal objects into the ear.
- Applying Harsh or Irritating Products: Strong scrubs, alcohol-based toners, or untested treatments can worsen irritation.
- Ignoring Hygiene: Overlooking regular ear cleaning or failing to sanitize ear-contact items propagates blackhead formation.
- Misidentifying Ear Lesions: Not all ear bumps are blackheads; underlying skin disorders like discoid lupus may mimic their appearance but require medical attention.
Home Care vs. Professional Treatment
| Feature | Home Care | Professional Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Safety | Safe for mild cases, avoids ear canal | Highly safe, performed under sterile conditions |
| Effectiveness | Works for surface ear blackheads | Suitable for persistent, severe, or tricky spots |
| Tools Used | Cleanser, toner, warm cloth | Blackhead extractor, prescription meds |
| Risks | Possible irritation, incomplete removal | Minimal; supervised for complications |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Can I use my regular facial skincare products on my ears?
A: Yes, gentle cleansers and exfoliants compatible with facial skin can be used on the outer ear. Avoid strong acids or granules close to the ear canal.
Q: How often should I clean my ears to prevent blackheads?
A: Clean the outer ear daily or every other day with a mild cleanser. Over-cleaning can strip essential oils and provoke sensitivity.
Q: Is it safe to extract blackheads inside the ear?
A: No. Never insert tools or perform extractions deep inside the ear. Only surface blackheads may be gently treated at home; otherwise, consult a dermatologist.
Q: What ingredients are recommended for preventing and treating ear blackheads?
A: Salicylic acid, glycolic acid, and witch hazel are dermatologist-approved ingredients for unclogging pores and preventing build-up.
Q: Do ear blackheads indicate a health problem?
A: Typically, ear blackheads are not a sign of serious illness; however, if accompanied by pain, swelling, or unusual presentation, consult a healthcare professional.
Conclusion
Blackheads on ears are a frequent yet manageable skin issue, resulting from excess oil production, poor hygiene, product residues, and hormonal fluctuations. Prevention centers on regular, gentle cleansing, avoiding bacterial transfer, and sensible product use. When blackheads appear, prioritize safe, non-invasive removal with chemical exfoliants and avoid risky extraction methods. For persistent or problematic cases, dermatological guidance is advised to avoid complications and secure healthy ears for the long term.
References
- https://mykaoshop.com/blogs/biore/blackheads-in-ear
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/321154
- https://www.bootshearingcare.com/lifestyle/spots-in-ear-causes-treatment/
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DimCw7zNVS0
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/22038-blackheads
- https://www.hollandandbarrett.com/the-health-hub/conditions/ear-nose-and-throat/blackheads-in-ears-advice/
Read full bio of medha deb












