Yellow Stool: Causes, Symptoms, Treatments, and When to Seek Help
Explore all about yellow stool, from dietary causes to medical conditions, and learn when it warrants medical attention.
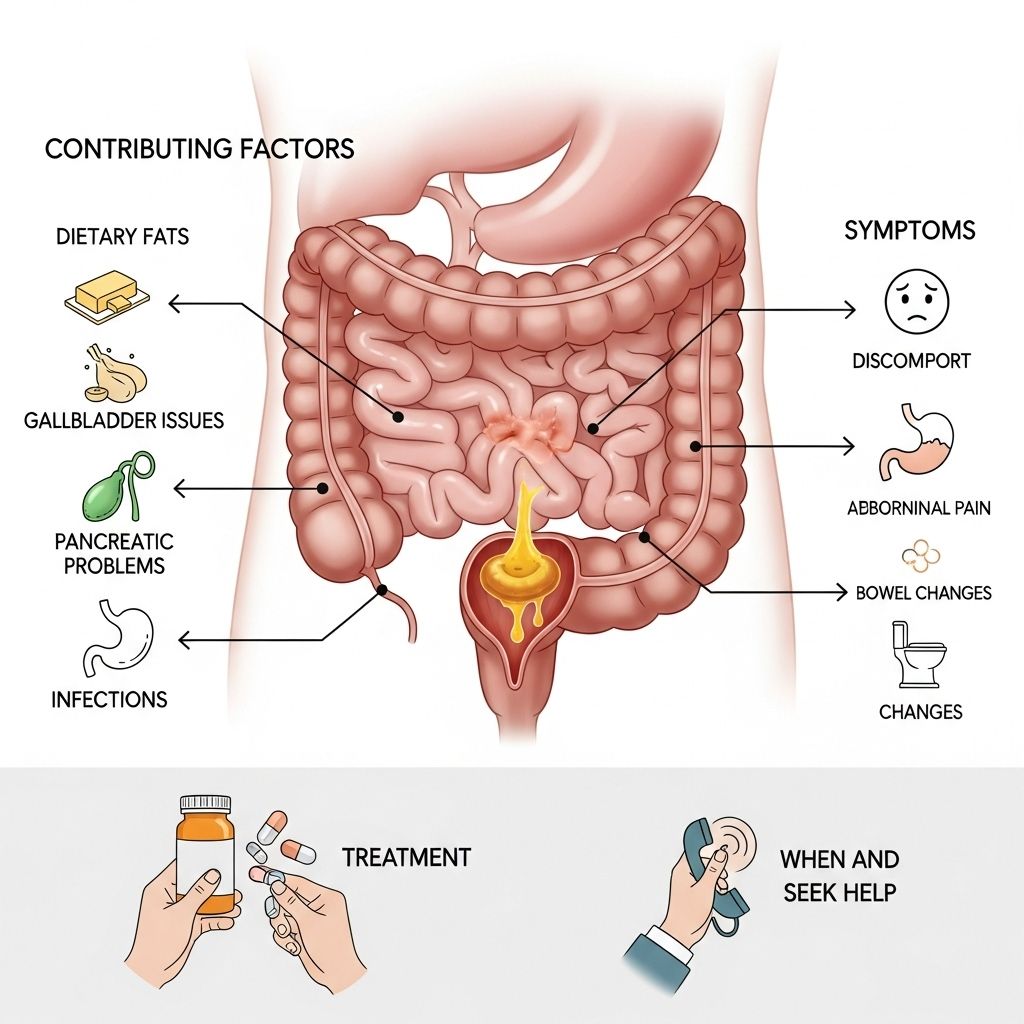
Understanding Yellow Stool
Stool color can offer important clues about your digestive health. Yellow stool is a common concern, surfacing due to a variety of reasons ranging from harmless dietary choices to underlying health conditions. In this article, we’ll explore the causes, symptoms, related disorders, diagnostic steps, treatment options, and guidance on when yellow stool may warrant medical attention.
What Is Yellow Stool?
Yellow stool refers to feces that are lighter or distinctly yellow in color. Normally, stool ranges from medium to dark brown, mainly due to bile and bilirubin breakdown. Yellow stool can be soft, hard, or even greasy, and it may be accompanied by other symptoms such as abdominal discomfort or diarrhea.
Causes of Yellow Stool
Several factors can turn stool yellow. These can be divided into two broad categories: dietary and medical causes.
Dietary Causes
- Food choices: Eating foods with high amounts of yellow pigments (like sweet potatoes, carrots), yellow food coloring, or consuming large amounts of fat can change stool color to yellow.
- Sudden diet changes: Alterations in the usual diet, especially an increase in high-fat foods, may temporarily result in yellow stool.
- Stress: Emotional stress can mildly impact digestion and alter stool color but rarely results in persistent yellow stool.
Medical Causes
- Pancreatic Disorders: Conditions like pancreatitis, pancreatic cancer, or duct blockage prevent proper digestion of fats, leading to yellow, often greasy stool known as steatorrhea.
- Gallbladder Diseases: Gallstones, cholecystitis (inflammation), or bile duct blockage can limit bile delivery, producing yellow stool.
- Liver Conditions: Hepatitis, cirrhosis, or other liver problems can disrupt bile salt production and pigment processing, causing pale yellow stools.
- Malabsorption Disorders: Diseases that interfere with absorption, such as celiac disease, Crohn’s disease (usually through terminal ileum damage), and chronic pancreatitis, can result in yellow, greasy, and foul-smelling feces.
- Intestinal Infections: Giardia parasite infection (giardiasis) often causes yellow diarrhea, cramps, and nausea. Gastroenteritis also temporarily produces yellow stools.
Summary Table: Common Causes and Features
| Cause | Features | Associated Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Diet | High-fat meals, yellow foods, coloring | Usually no other symptoms |
| Pancreatic Disease | Steatorrhea, greasy stool | Abdominal pain, weight loss |
| Gallbladder Disease | Bile blockage, pale yellow stool | Jaundice, abdominal pain |
| Liver Disease | Disrupted pigment processing | Fatigue, jaundice |
| Malabsorption | Greasy, foul-smelling stool | Nutrient deficiencies |
| Infection (Giardiasis) | Bright yellow diarrhea | Cramping, nausea |
Yellow Stool and Specific Health Conditions
Crohn’s Disease
- Yellow stool is not a primary symptom but can occur due to malabsorption, fat not being absorbed as it should.
- Mucus coating in stool, appearing yellow or white, is common in Crohn’s.
- Persistent yellow stool may indicate issues in the pancreas, liver, or gallbladder, not solely Crohn’s disease.
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
- Yellow stool is not directly caused by IBS but may result from dietary patterns or co-existing malabsorption issues.
Liver and Gallbladder Disorders
- Conditions that block bile flow, such as gallstones or liver scarring (cirrhosis), prevent breakdown of pigments, resulting in pale yellow stool.
- Other symptoms may include jaundice (yellowing of skin and eyes), fatigue, fever, and abdominal pain.
Malabsorption Disorders
- Celiac disease and related disorders damage intestinal lining, reducing nutrient absorption and causing fatty, yellow, foul-smelling stool.
- Symptoms often worsen after consuming gluten in sensitive individuals.
Giardiasis and Intestinal Infections
- Giardia parasite induces rapid food transit, cramps, diarrhea, and bright yellow stool.
- Gastroenteritis from viruses or bacteria can also cause transient yellow diarrhea.
Yellow Stool in Children
Children may occasionally produce yellow stool, but persistent yellow diarrhea could signal an underlying issue such as:
- Toddler’s diarrhea—often related to high sugar and fluid intake, low fat diet
- Malabsorption—secondary to celiac, Crohn’s, or pancreatic dysfunction
- Infection—parasitic (giardiasis) or viral
- Lactose intolerance or food allergy
- Other digestive disorders—e.g., ulcerative colitis, overactive thyroid
If yellow diarrhea is persistent in a child, it is important to consult a pediatrician for diagnosis and treatment.
Symptoms Often Associated with Yellow Stool
Depending on the cause, yellow stool may be accompanied by other symptoms, which can help identify the underlying issue:
- Abdominal pain or cramping
- Foul odor and greasy texture (steatorrhea)
- Diarrhea or loose stool
- Fatigue and weakness
- Nausea or vomiting
- Jaundice (yellowing of eyes or skin)
- Unintentional weight loss
- Dark urine
- Fever (in cases of infection)
- Itching (with liver or biliary conditions)
When to See a Doctor
- Yellow stool lasting more than a few days
- Accompanied by severe abdominal pain, fever, persistent diarrhea, or vomiting
- Presence of jaundice or dark urine
- Fatigue, unexplained weight loss
- Recent history of digestive disease (Crohn’s, celiac, IBS) with new yellow stools
- Yellow stool in children that does not resolve quickly
Prompt evaluation is especially important if yellow stool is associated with pain, jaundice, dehydration, or other systemic symptoms.
Diagnosis of Yellow Stool Causes
Diagnosis involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and tests:
- Review of diet, medication, and recent travel
- Physical exam focused on abdominal organs
- Blood tests: liver function, pancreatic enzymes, signs of infection
- Stool analysis: for parasites, fat content, blood, infection
- Imaging: ultrasounds or CT for liver/gallbladder/pancreas assessment
- Specialized tests: for celiac, Crohn’s, or bile duct obstruction
Treatment for Yellow Stool
Treatment targets the underlying cause:
- Dietary adjustments: Reduce fatty foods, artificial colorings, balance fiber intake
- Pancreatic support: Enzyme supplements if needed
- Liver and gallbladder disorders: Management of hepatitis, removal of gallstones, anti-inflammatory agents
- Treatment of malabsorption: Gluten-free diet (celiac), nutrition/medication adjustments (Crohn’s)
- Infection: Antibiotics or anti-parasitic agents for giardiasis and related infections
- Pediatric management: Tailored to cause, such as fluid adjustments or elimination diets
Supportive measures include maintaining hydration, correcting nutritional deficiencies, and regular monitoring.
Prevention Tips
- Maintain a balanced diet rich in fiber
- Avoid excessive use of fatty foods and artificial colors
- Practice good hygiene to avoid gastroenteritis and giardiasis
- Seek regular medical guidance if you have known malabsorption or digestive disorders
- Monitor children’s diet for excessive sugar and low fat intake
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What does yellow stool mean?
Yellow stool may reflect dietary intake, but it can also signal medical problems like malabsorption, infection, or bile flow obstruction. Persistent or symptomatic yellow stool warrants medical evaluation.
Is yellow stool always dangerous?
No, a single episode is rarely serious, especially after eating pigmented or fatty foods. However, if it persists or is accompanied by other symptoms (pain, jaundice, fever), it could reflect an underlying health problem.
How is yellow stool different from normal stool?
Normal stool is brown due to bile pigment breakdown. Yellow stool is paler because of excess undigested fat, rapid food transit, or lack of bile pigment from liver/gallbladder/pancreatic dysfunction.
Can stress cause yellow stool?
Stress can alter digestive motility and sometimes affect stool color, but it rarely causes persistent yellow stool without other causes.
Should children with yellow stool be seen by a doctor?
Occasional yellow stool is common. Persistent yellow diarrhea, especially with other symptoms, should be evaluated by a pediatrician to rule out infection, malabsorption, or other digestive disorders.
Can food allergies cause yellow stool?
Yes, in some cases, especially in children, food allergies or intolerances such as lactose intolerance may result in yellow stool. A healthcare provider can help determine the root cause.
Will changing my diet help?
If dietary cause is suspected, reducing fatty foods, artificial colors, and balancing fiber intake may resolve yellow stool. Persistent symptoms require further investigation.
Key Takeaways
- Diet, digestion, and medical conditions all influence stool color
- Yellow stool may not always signal disease; context and symptoms matter
- Persistent, foul-smelling, greasy, or symptomatic yellow stool suggests malabsorption, liver, gallbladder, pancreatic, or intestinal problems and requires medical attention
- Timely evaluation and targeted treatment are crucial, especially for children and individuals with other symptoms
References
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/crohns-disease-and-yellow-stools
- https://www.healthline.com/health/yellow-stool-ibs
- https://resources.healthgrades.com/right-care/digestive-health/yellow-poop
- https://www.healthcentral.com/digestive-health/yellow-poop
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/323147
- https://www.narayanahealth.org/blog/yellow-poop-causes-meaning-and-treatment
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/diarrhea/expert-answers/stool-color/faq-20058080
- https://health.clevelandclinic.org/yellow-diarrhea
- https://www.piedmont.org/living-real-change/what-your-stool-says-about-your-health
Read full bio of Sneha Tete












