Warning Signs and Symptoms of Clogged Arteries
Recognize early warning signs and symptoms of clogged arteries to prevent life-threatening heart and vascular conditions.
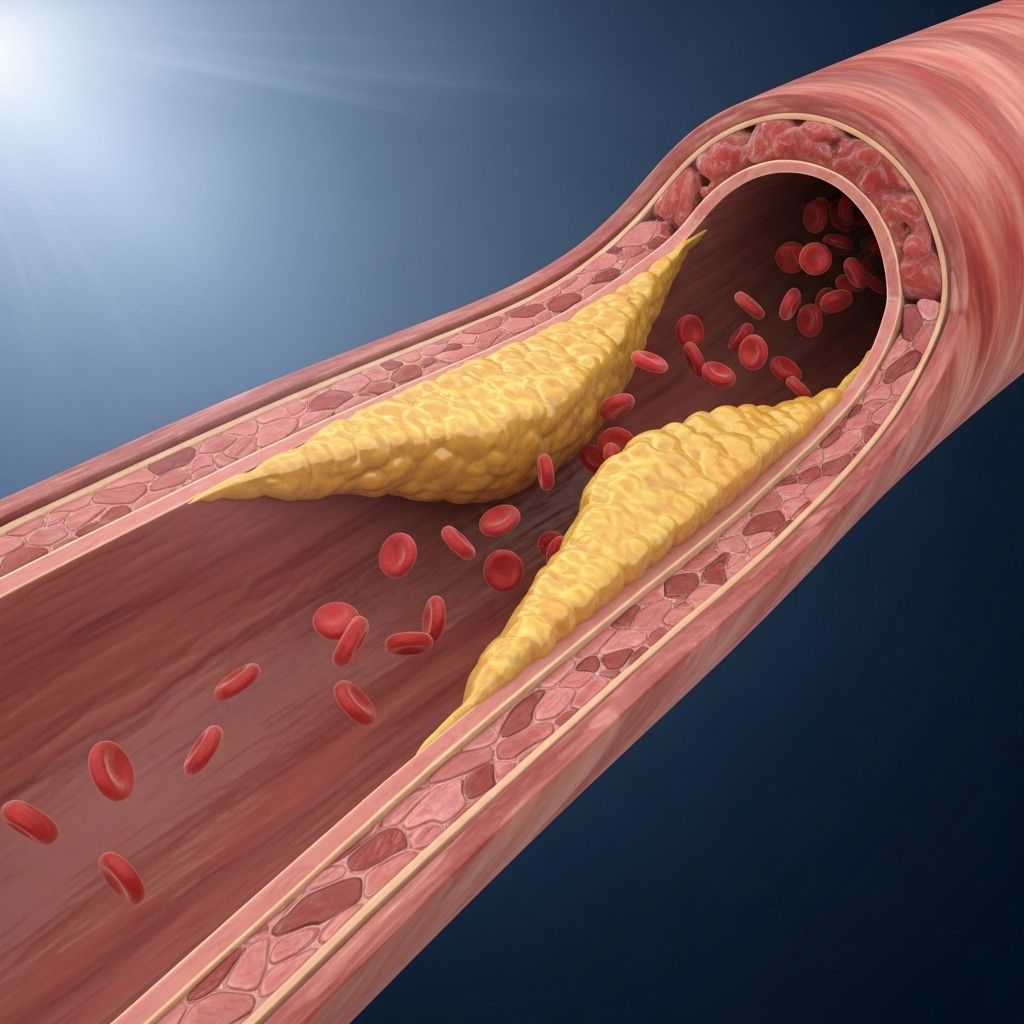
Clogged arteries are a critical health concern, threatening the flow of blood and oxygen to essential organs and tissues. Early detection of warning signs can prevent severe outcomes such as heart attacks, strokes, or limb damage. This comprehensive guide explores the causes, early indicators, and emergency symptoms of artery blockages in the heart, brain, legs, and other affected regions.
What Are Clogged Arteries?
Arteries are blood vessels that deliver oxygen-rich blood throughout the body. When they become narrowed or blocked—often by a gradual buildup of fats, cholesterol, and other substances known as plaques—the flow is restricted. This process, called atherosclerosis, can affect arteries in the heart, brain, limbs, or other organs and may lead to life-threatening events like coronary artery disease (CAD) or stroke.
Early Signs and Symptoms of a Clogged Artery
Symptoms of clogged arteries may emerge slowly, sometimes unnoticed until the blockage becomes severe. It’s crucial to recognize the different indicators, which vary depending on the affected area.
Clogged Coronary Arteries: Impact on the Heart
The heart is highly vulnerable to clogged arteries. The most common outcome is coronary artery disease (CAD), where plaques build in the coronary arteries, potentially leading to a heart attack.
- Chest pain (angina): Often radiates into the neck, jaw, arm, or back and may feel like squeezing, pressure, or heaviness.
- Sweating
- Shortness of breath
- Dizziness
- Heart palpitations (racing or fluttering)
- Nausea
- Weakness
- Syncope (sudden loss of consciousness)
Most people feel angina during physical exertion or emotional distress; it typically subsides with rest or calming down. In contrast, chest pain that persists at rest could indicate a heart attack and needs immediate medical attention.
Clogged Cerebral Arteries: Stroke Warning Signs
Blockages in the arteries supplying the brain can cause an ischemic stroke. Recognize these symptoms urgently, as untreated strokes can rapidly cause permanent damage.
- Facial drooping
- Slurred speech
- Balance problems
- Vision changes
- Sudden loss of consciousness
Stroke symptoms often affect specific functions controlled by the blocked brain region, such as movement, sensation, or vision. Quick response is vital, as every second counts in reducing brain tissue loss.
Peripheral Artery Disease: Blockages in the Legs
When arteries in the limbs, especially the legs, become narrowed or clogged, this is referred to as Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD). Warning signs may surface over years, but the following symptoms are especially important to look for:
- Claudication: Aching, pain, or tiredness in the calf, thigh, or buttocks during walking/activity, relieved by rest. As PAD gets worse, pain may even occur during rest.
- Cold feet
- Pale legs when raised
- Foot sores that don’t heal
- Impotence in men
- Persistent sensations (burning, tiredness, or pain) while walking
- Numbness in legs or feet when resting
- Leg pain at night
PAD may be present without symptoms, especially in early stages. Seek medical advice if experiencing any combination of the above to ensure proper diagnosis and treatment.
Other Common Areas Affected
Clogged arteries can also impact:
- Retinal arteries: Vision changes or sudden visual loss.
- Kidney arteries: Altered urination or kidney function.
- Other arteries: Cold hands or feet, skin color changes, or erectile dysfunction.
Prompt attention to any unusual, unexplained symptoms is essential for preventing further damage.
Emergency Symptoms: When to Seek Immediate Care
Certain symptoms point to a medical emergency and require urgent professional intervention. If you or someone around you experiences any of the following, call emergency services immediately:
- Severe chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Sudden loss of consciousness
- Acute numbness, paralysis, or facial droop
- Sudden vision loss
Delaying treatment can result in irreversible damage to the heart, brain, or other organs.
What Causes Clogged Arteries?
The most common underlying cause is atherosclerosis—a condition where cholesterol, fat, and other substances accumulate and harden inside the artery walls.
- High cholesterol levels
- High blood pressure
- Smoking
- Diabetes
- Obesity and physical inactivity
- Unhealthy diet
- Genetics or family history
Over time, this gradual build-up leads to narrowing and stiffening, restricting blood flow and increasing risk.
How Are Blocked Arteries Diagnosed?
Early diagnosis is key to preventing complications. Healthcare providers may use a combination of symptoms, physical exams, and diagnostic tests to identify artery blockages.
- Listening for a bruit—a whooshing sound heard through a stethoscope
- Checking for absent or weak pulses in specific arteries or limbs
- Measuring blood pressure differences between limbs
- Laboratory tests (like cholesterol panels)
- Imaging tests (ultrasound, CT angiography, or MRI)
- Electrocardiogram (EKG) for heart function
Based on the findings, medical professionals can pinpoint the location, severity, and potential risks of the blocked arteries.
Comparison Table: Typical Symptoms by Affected Artery Region
| Artery Location | Common Symptoms | Emergency Signs |
|---|---|---|
| Coronary (Heart) | Chest pain, shortness of breath, sweating, dizziness | Persistent chest pain, collapse, severe shortness of breath |
| Cerebral (Brain) | Facial drooping, slurred speech, vision changes, confusion | Sudden paralysis, coma, sudden vision loss |
| Peripheral (Legs) | Leg pain on walking, cold feet, sores, pale skin | Non-healing sores, critical limb ischemia |
| Retinal/Kidney | Vision changes, urination changes | Sudden blindness, severe kidney dysfunction |
What Should You Do If You Notice Symptoms?
Do not ignore persistent or unusual symptoms. Timely medical consultation can save lives and prevent irreversible organ damage. Discuss all changes with your healthcare provider, especially if you have risk factors for artery disease.
- Report symptoms to your doctor promptly.
- Monitor changes, including pain location, intensity, and what triggers or relieves it.
- Maintain regular health check-ups—catching disease early makes treatment easier and outcomes better.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are early warning signs of clogged arteries in the heart?
A: Early warning signs include chest pain (angina), shortness of breath, sweating, and dizziness, especially triggered by exercise or emotional stress.
Q: How does angina differ from a heart attack?
A: Angina is chest pain that usually goes away with rest or calming down, while heart attack pain often persists or worsens at rest, usually requiring urgent care.
Q: What symptoms point to a blocked artery in the brain (stroke)?
A: Symptoms such as facial droop, slurred speech, vision changes, difficulties with balance, and loss of consciousness—especially if sudden—should be treated as a medical emergency.
Q: What are signs of blocked arteries in the legs?
A: Look for pain or cramps when walking (claudication), cold or numb legs or feet, pale skin, and sores or ulcers that don’t heal.
Q: Can someone have blocked arteries without symptoms?
A: Yes, many people remain asymptomatic until blockages are severe enough to impair blood flow or trigger an emergency like a heart attack or stroke.
Action Steps to Lower Your Risk
- Eat a heart-healthy, low-cholesterol diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Exercise regularly—aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate activity per week.
- Avoid smoking or excessive alcohol consumption.
- Manage chronic conditions such as high blood pressure, diabetes, and high cholesterol.
- Maintain a healthy weight and manage stress.
Your doctor can guide you in tailoring risk reduction strategies to your health profile.
Key Takeaways
- Clogged arteries result from gradual plaque buildup called atherosclerosis that restricts blood flow.
- Symptoms vary by location—angina and chest pain for the heart, neurological changes for the brain, claudication and numbness for legs, and other changes for retinal or kidney arteries.
- Any persistent, severe, or unexplained symptoms need prompt evaluation to avoid life-threatening consequences.
- Healthy lifestyle choices reduce your risk and protect cardiovascular health.
References
- https://www.healthline.com/health/heart-health/what-are-the-warning-signs-of-clogged-arteries
- https://www.advocatehealth.com/health-services/advocate-heart-institute/programs-and-treatments/coronary-artery-disease-program/blocked-artery-symptoms
- https://michiganvascularcenter.com/what-are-the-warning-signs-of-a-blocked-artery-in-the-leg/
- https://www.aurorahealthcare.org/services/heart-vascular/conditions/coronary-artery-disease/blocked-artery-symptoms
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/16753-atherosclerosis-arterial-disease
- https://utswmed.org/medblog/blocked-artery/
- https://www.bhf.org.uk/informationsupport/heart-matters-magazine/medical/blocked-arteries
- https://www.webmd.com/heart-disease/clogged-arteries-arterial-plaque
- https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/atherosclerosis/symptoms
Read full bio of Sneha Tete












