How Long Does It Take to Get Rid of Lice?
Learn how long it takes to eliminate head lice, effective treatments, symptoms, and prevention for families.
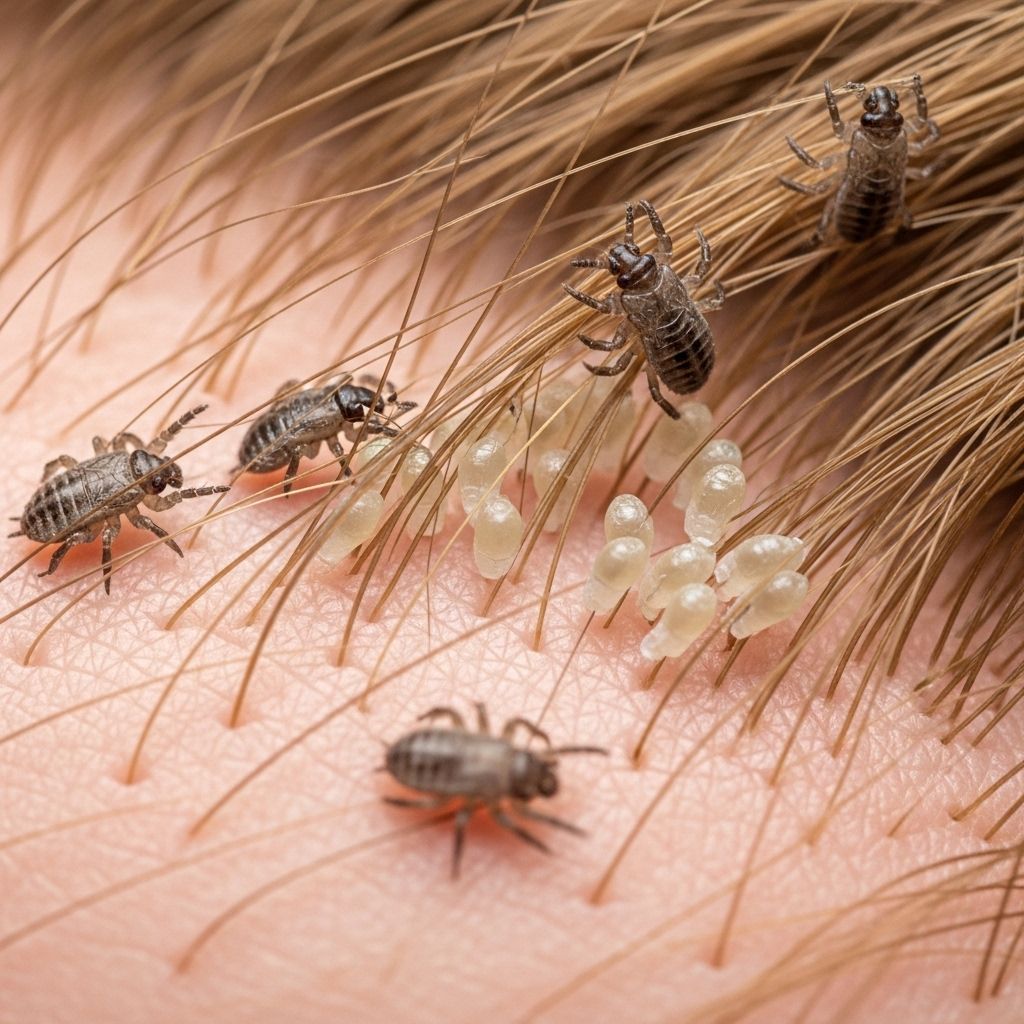
Getting rid of head lice requires patience, consistent treatment, and proper aftercare. While some treatments kill mature lice immediately, fully eradicating an infestation—including their eggs (nits)—generally takes 2 to 3 weeks. This article explores the lice life cycle, symptoms, treatment strategies, prevention methods, and answers common questions for caregivers and patients.
What Are Lice?
Lice are tiny, parasitic insects that live on the human scalp and feed on blood. They are most common in children aged 3–11, though anyone in close contact can become infested. Lice are not a sign of poor hygiene and cannot jump or fly, but spread through direct contact or sharing items like brushes and hats.
- Size: 2–3 millimeters
- Transmission: Direct head-to-head contact or shared personal items
- Common hosts: Children, though anyone can get them
- Lice do not live on pets
Types of Lice
- Head lice: Most common, present on the scalp
- Body lice: Found on the body and clothing
- Pubic lice: Infest the genital area
Lice Life Cycle: Why Multiple Treatments Are Needed
Understanding the lice life cycle is crucial for successful removal. The life cycle includes three stages: egg (nit), nymph, and adult.
| Stage | Description | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Egg (Nit) | Eggs are laid near the scalp and are oval, yellow or white. They adhere tightly to hair shafts. | Hatch in 7–10 days |
| Nymph | Immature lice emerge from eggs; smaller and less mobile. | Develop into adults in 9–12 days |
| Adult | Full-grown lice are about sesame seed-sized and live near the scalp. | Live up to 30 days on scalp |
Female lice lay up to 6 eggs per day, meaning infestations can grow rapidly and repeated treatment is essential to kill newly hatched lice.
Symptoms of Lice Infestation
Lice infestations often present with characteristic symptoms, though some individuals remain asymptomatic for weeks.
- Itching, tingling, or tickling on the scalp
- Visible lice moving in the hair
- Nits (eggs) attached to hair shafts
- Red bumps or sores from scratching
Detecting live lice is necessary for a definitive diagnosis. The presence of nits alone doesn’t confirm active infestation.
How Do People Get Lice?
Lice spread mainly by direct head-to-head contact—children are at greater risk during play, sleepovers, family gatherings, or group activities. Less commonly, lice transfer through shared items (brushes, hats, pillows), but they cannot survive more than 24 hours off the human scalp.
- Most common environments: Family events, playdates, sleepovers
- Less frequent at schools compared to home or social gatherings
How Long Does It Take to Get Rid of Lice Completely?
Complete lice eradication normally requires 2–3 weeks of careful treatment and follow-up. Most products kill live lice but not nits, so reapplication is needed after eggs hatch.
- Single treatment: Kills mature lice, but eggs may survive
- Multiple treatments: Required to kill newly hatched lice before they reach adulthood and lay more eggs
- After treatment: Check hair every 2–3 days for 2–3 weeks and remove dead lice & nits
The timeline may vary based on the product used, thoroughness of application, and adherence to instructions. Some prescription medications kill both lice and eggs; in those cases, one treatment may be enough.
Overview of Treatment Options
Treating lice can be accomplished with over-the-counter medications, prescription drugs, or home techniques like wet combing. All household members and close contacts who share a bed or clothing with the infested person should be checked and treated at the same time.
Medicated Treatments
- Permethrin (Nix): Safe for ages 2 months+, widely used over-the-counter option
- Pyrethrin: Derived from chrysanthemum flowers, OTC option, ages 2 years+
- Spinosad: Prescription, kills both lice and eggs, retreatment not always necessary
Application Directions
- Remove or protect clothing before applying medication
- Pay close attention to instructions (application time and washing out)
- Use enough medication (additional bottle may be needed for long hair)
- Have the infested person put on clean clothes after treatment
Follow-Up Care
- Use a fine-tooth or flea comb to remove dead lice and nits every 2–3 days for 2–3 weeks
- Repeat the treatment 7–10 days after the first application (unless using an egg-killing product or directed differently by doctor)
- If slow-moving lice remain 8–12 hours after treatment, do not reapply; use a comb to physically remove them
- If no dead lice are found after first treatment or if lice remain active, consult with a healthcare provider to switch medication
Home Remedies
- Wet combing: Dampen hair, divide into sections, and use a nit comb to remove lice and eggs manually
- Can be time-consuming, typically performed every 3–4 days for several weeks
- Smothering/dehydrating: Some people try oils or products to asphyxiate lice, but this is less reliable than medicated options
Prevention Strategies
- Avoid head-to-head contact during play or activities
- Do not share personal items such as hats, combs, scarves, towels, or headphones
- Wash bedding, clothing, and plush toys in hot water and dry at high heat during infestations
- Vacuum surfaces and furniture where infested individuals have rested
- Regularly check hair of children, especially after sleepovers or group activities
Routine cleaning of the home is important but do not overdo disinfecting: lice do not live long away from the scalp, and excessive chemical use is unnecessary.
Common Concerns and Misconceptions
- Lice are not a sign of poor hygiene or disease.
- Lice infestations are strictly a human-to-human issue; pets do not play a role.
- Nits alone do not mean live lice. Successful eradication means no living lice are found after repeated checks and treatments.
When to Consult a Healthcare Provider
- Symptoms persist despite proper treatment and follow-up
- Allergic reactions or severe skin irritation present
- Lice appear resistant to over-the-counter medication
- For children under age 2, pregnant individuals, or those with chronic skin conditions
Some products are unsuitable for very young children or those with specific medical histories. Always seek professional advice if uncertain about next steps.
Aftercare: Cleaning Up and Preventing Reinfection
- Launder all clothing, bedding, and towels used two days before treatment in hot water (at least 130°F) and tumble dry at high heat
- Items that cannot be washed: Seal in a plastic bag for two weeks or vacuum thoroughly
- Check for lice: Continue checking household members and repeat treatment cycles as necessary
- Personal items: Clean combs, brushes, hats, hair accessories by soaking in hot water for 5–10 minutes
Lice cannot survive more than 24 hours off the human host, so excessive cleaning of household surfaces generally isn’t needed.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: How long does it take to fully remove lice?
A: It typically takes 2 to 3 weeks using repeated treatments, thorough combing, and careful hygiene. Each medication may vary in instructions.
Q: Can lice live on pets or furniture?
A: No. Lice only live on humans, especially on the scalp. They cannot infest pets or survive long periods on furniture.
Q: How do I know if the lice are gone?
A: After treatment and two weeks of regular checking and combing, if no live lice or new nits are found, the infestation is likely resolved. Continue monitoring for up to 3 weeks.
Q: What if lice resist OTC treatments?
A: Contact a healthcare provider. Sometimes, lice become resistant to common treatments, and prescription medication may be necessary.
Q: Do lice always cause itching?
A: Not always. Some people may not feel symptoms for weeks even with active infestation. Searching for live lice and nits is critical.
Key Takeaways
- Lice are highly contagious and require multiple treatments for complete removal.
- Successful eradication can take up to 3 weeks with proper treatment and frequent combing.
- Consult a healthcare provider if standard treatments fail or if special health circumstances exist.
- Good hygiene and regular checks in at-risk groups are the best prevention methods.
References
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/how-long-does-it-take-to-get-rid-of-lice
- https://www.cdc.gov/lice/treatment/index.html
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/lice/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20374404
- https://www.healthline.com/health/lice/how-long-do-lice-live
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2724133/
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/318026
- https://www.kidshealth.org.nz/head-lice
- https://info.health.nz/keeping-healthy/healthy-homes-environments/pests-and-insects/head-lice-nits
Read full bio of Sneha Tete












