Dilation and Curettage (D&C): Procedure, Uses, Risks & Recovery
Comprehensive guide to Dilation and Curettage (D&C), including procedure steps, uses, recovery, potential risks, and answers to common questions.
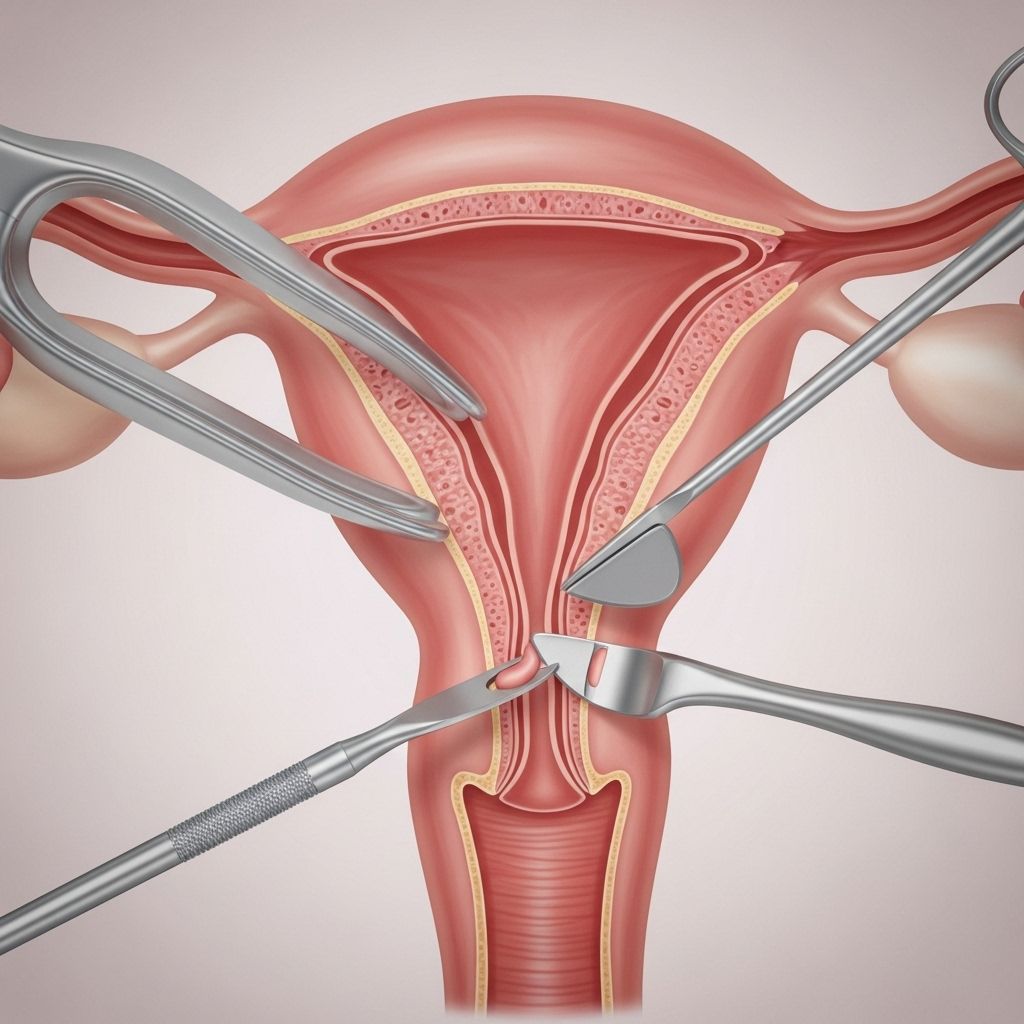
Dilation and Curettage, widely known as D&C, is a common gynecologic surgical procedure performed to diagnose or treat conditions affecting the uterus. This in-depth guide provides insight into the procedure, when and why it’s recommended, what to expect during and after the process, associated risks, and commonly asked questions.
What Is Dilation and Curettage (D&C)?
Dilation and Curettage (D&C) is a minor surgical procedure involving two primary steps: dilation, which is the opening of the cervix, and curettage, the removal of tissue from the lining of the uterus (endometrium), often with a specialized instrument known as a curette. The objective is to diagnose or address conditions causing abnormal uterine symptoms or to remove tissue after certain reproductive events.
Why Is a D&C Performed?
D&C can be used for both diagnostic and therapeutic reasons. Depending on the patient’s condition, it may be necessary to:
- Assess abnormal or heavy uterine bleeding, such as unexplained or persistent menstrual bleeding (menorrhagia), bleeding between periods, or bleeding after menopause.
- Investigate uterine infections or evaluate for suspected endometrial conditions.
- Diagnose uterine cancer, polyps, or fibroids.
- Investigate causes of infertility or abnormal Pap smear results.
- Treat certain conditions:
- Clear tissue after an incomplete miscarriage (retained products of conception).
- Remove pieces of placenta that remain post-delivery, preventing infection or excessive bleeding.
- Remove benign growths such as polyps or small fibroids.
- Treat excessive bleeding that does not respond to medication.
Less commonly, D&C may be used as part of fertility testing or the investigation of persistent pelvic pain.
Types of D&C
- Diagnostic D&C: Removes a small sample of endometrial tissue for laboratory evaluation, most often to diagnose a cause for abnormal bleeding or confirm/rule out endometrial (uterine lining) cancer.
- Therapeutic D&C: Removes larger amounts or all of the uterine contents, often after an incomplete miscarriage, retained placenta, or to treat abnormal bleeding.
Alternative and Related Procedures
In some situations, a D&C is performed alongside or instead of other procedures, such as:
- Endometrial biopsy: Uses an aspiration device to collect a sample—often less invasive than a D&C for diagnosis.
- Hysteroscopy: Involves using a slender device with a camera to visualize the uterine interior, which may be performed in conjunction with a D&C for better assessment and precision.
- Dilation and Evacuation (D&E): Used for pregnancies later than 14 weeks, involving removal of fetal or placental tissue.
Who Might Need a D&C?
D&C is considered for women who experience:
- Unexplained abnormal uterine bleeding
- Painful periods or severe cramps not responsive to other treatments
- Postmenopausal bleeding
- Incomplete miscarriage or termination of pregnancy
- Polyps, fibroids, or uterine abnormalities discovered during imaging or exams
- Suspected uterine infection or cancer based on symptoms and test results
Preparing for a D&C Procedure
Before scheduling a D&C, your doctor will review your medical history, medications, allergies, and results from blood or imaging tests. You may be asked to:
- Undergo a pregnancy test and/or blood work.
- Avoid eating or drinking after midnight if the procedure is scheduled with general anesthesia.
- Arrange transportation home, as sedatives or anesthesia may be used.
- Stop certain medications (such as anticoagulants or anti-inflammatory agents) as directed by your healthcare provider.
- Discuss your current health status, including possible signs of infection.
Feel free to ask your healthcare team about what to expect, pain management options, or concerns regarding fertility and future cycles.
How Is a D&C Performed?
The procedure is typically brief (less than 30 minutes) and may take place at a hospital, surgical center, or outpatient clinic. Here is a step-by-step overview of what usually happens:
- Anesthesia: You will receive either general, regional (spinal), or local anesthesia with sedation to ensure comfort.
- Positioning and Examination: You’ll lies on your back in a position similar to a pelvic exam, with feet placed in stirrups.
- Speculum Insertion: A speculum is gently inserted into your vagina to allow access to the cervix.
- Cervical Preparation:
- If the cervix is tight or requires more dilation, the doctor may insert laminaria (thin rods that gradually absorb fluid and expand) or use medication (such as misoprostol) beforehand to facilitate gentle dilation.
- The cervix may be held in place with a clamp.
- Dilation: The healthcare provider uses graduated rods or dilators to widen the cervical canal.
- Curettage: A curette (either a small spoon-shaped instrument or a suction device) is used to gently remove the uterine tissue or contents.
- Other Procedures: A hysteroscope may be inserted to guide the curettage and allow for removal of polyps or fibroids if needed.
- Completion: Once complete, the removed tissue is sent to a laboratory for further analysis, especially when D&C is used to diagnose suspicious symptoms.
Table: Steps of a Standard D&C Procedure
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Anesthesia | Pain relief provided by general, regional, or local anesthesia with sedation. |
| Positioning | Patient reclined, legs in stirrups, similar to a pelvic examination. |
| Speculum Insertion | Allows visualization and access to the cervix. |
| Cervical Preparation | Dilators or medication may be used to open the cervix. |
| Dilation | Gradually widening the cervical opening for instrument access. |
| Curettage | Removal of endometrial tissue using a curette or suction device. |
| Sample Collection | Tissue is sent to a lab for microscopic evaluation when indicated. |
What to Expect After the Procedure
Following a D&C, patients are typically monitored in a recovery area for several hours, especially if sedation or anesthesia was used. Most individuals can return home the same day. Normal reactions during recovery may include:
- Mild cramping or pelvic discomfort
- Light spotting or vaginal bleeding for a few days to two weeks
Your healthcare provider will give you specific instructions regarding:
- Use of sanitary pads (not tampons) until bleeding stops
- Avoidance of sexual intercourse and douching until cleared
- Rest and gradual resumption of routine activities as tolerated
- Pain management using over-the-counter medication as advised
Your next menstrual period may occur later than usual as the uterus regenerates its lining.
Possible Risks and Complications
While D&C is considered a safe and routine procedure, as with any surgical intervention, it carries some risks. Complications are rare but may include:
- Infection, such as endometritis (inflammation of the uterine lining)
- Heavy or prolonged bleeding, blood clots
- Injury to the uterus, cervix, or nearby organs: Accidental puncture or laceration is uncommon
- Scar tissue (Asherman’s syndrome), which may cause menstrual changes or, rarely, fertility issues
Contact your healthcare provider promptly if you experience:
- Heavy or persistent bleeding (soaking through more than one pad an hour)
- Severe abdominal or pelvic pain not relieved by medication
- Fever or chills
- Foul-smelling vaginal discharge
- Signs of infection
Prompt attention can help identify and manage any rare complications.
Recovery and Aftercare
Most patients recover quickly, often returning to normal activities within a day or two. Key aftercare instructions include:
- Rest as needed, especially on the day of surgery
- Take medications (such as pain relievers or antibiotics) as prescribed
- Avoid heavy lifting and strenuous activity for several days
- Do not use tampons, douche, or engage in intercourse until bleeding has completely stopped and your doctor confirms it is safe (typically 2 weeks)
- Schedule and attend your follow-up appointment to discuss laboratory results and ongoing care
Resuming Normal Activities and Future Fertility
D&C generally does not affect fertility or the ability to have healthy pregnancies in the future unless complications develop. Most patients return to their routines within 1–2 days. Sexual intercourse, tampon use, and swimming should be avoided until your provider says it is safe—usually once vaginal bleeding and discharge have resolved.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Is D&C a major surgery?
A: No. D&C is a minor, minimally invasive procedure typically performed on an outpatient basis with a rapid recovery time.
Q: Will I feel pain during or after the procedure?
A: While you may feel mild cramping after the procedure, anesthesia ensures you are comfortable during the process. Pain is usually mild and managed with over-the-counter medications.
Q: How soon can I return to normal activities after a D&C?
A: Light activities can typically resume a day after the procedure. Avoid strenuous activities, tampons, and intercourse until cleared by your physician.
Q: Can a D&C affect my fertility?
A: It very rarely affects fertility. If complications, such as Asherman’s syndrome (excessive scarring), develop, further evaluation and treatments are available. Discuss any concerns with your doctor.
Q: What are warning signs I should watch for after D&C?
A: Call your doctor if you have fever, heavy bleeding, severe abdominal pain, foul-smelling vaginal discharge, or any symptoms that concern you.
When to Call the Doctor
- Excessive or persistent vaginal bleeding (soaking a pad per hour for more than 2 hours)
- Severe abdominal pain, not relieved by pain medications
- Fever above 100.4°F (38°C)
- Foul-smelling vaginal discharge
- Signs or symptoms of infection (chills, malaise)
Summary
Dilation and Curettage (D&C) remains a safe, well-tolerated, and effective diagnostic or therapeutic procedure for women experiencing uterine concerns. With proper guidance and follow-up, most individuals recover rapidly and resume normal life.
References
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1IwrAyonFA4
- https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/conditionsandtreatments/dilatation-and-curettage-dc
- https://www.webmd.com/women/d-and-c-dilation-and-curettage
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK568791/
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/procedures/dilation-and-curettage
- https://healthy.kaiserpermanente.org/health-wellness/health-encyclopedia/he.dilation-and-curettage-d-c.abq4501
- https://www.acog.org/womens-health/faqs/dilation-and-curettage
Read full bio of Sneha Tete












