Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Surgery: What to Expect, Procedure & Recovery
Learn about coronary artery bypass graft surgery, from preparation and procedure to risks, recovery, and post-surgical care.
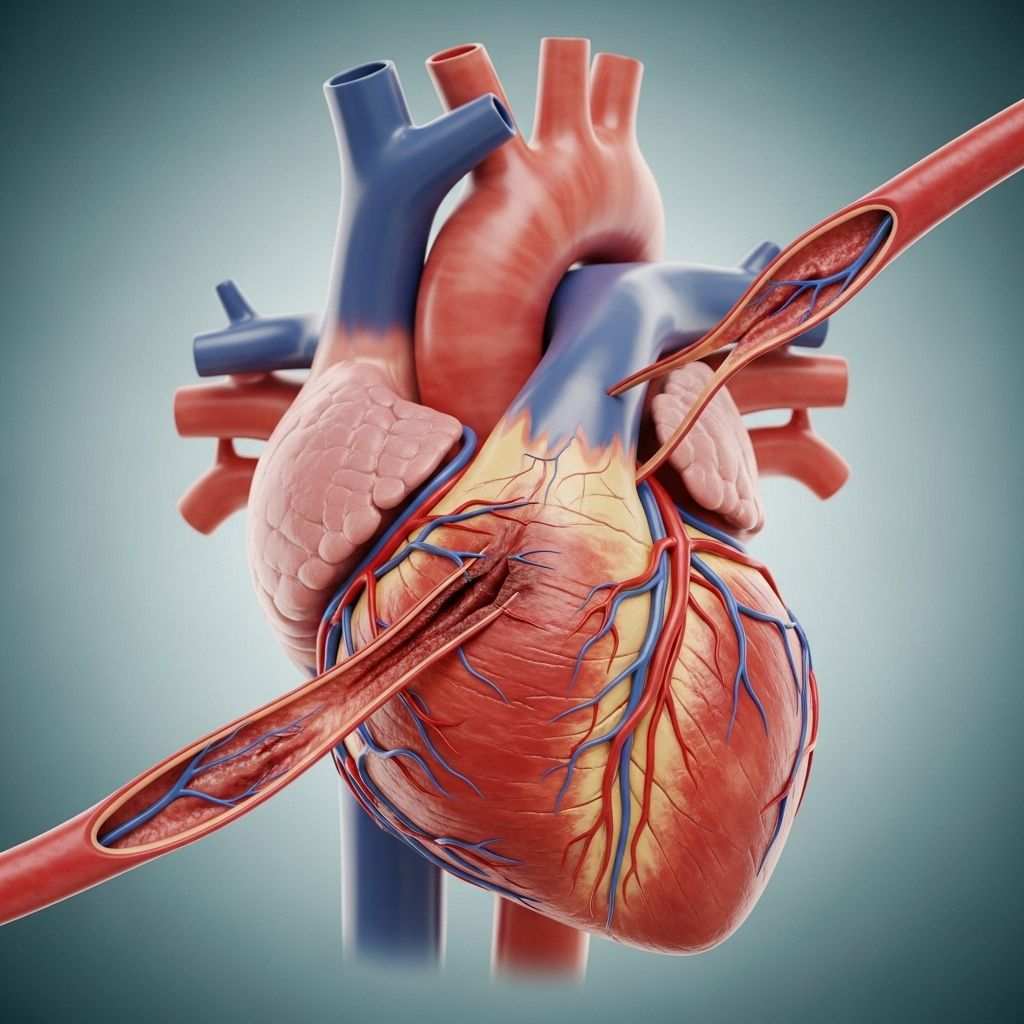
Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Surgery
Coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery is a major heart operation performed to improve blood flow to the heart muscle when coronary arteries are narrowed or blocked. It is commonly recommended in cases of severe coronary artery disease (CAD) and remains a standard treatment for restoring healthy circulation to cardiac tissues, preventing heart attacks, and reducing symptoms such as chest pain and shortness of breath.
What is Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG) Surgery?
CABG is a surgical procedure where one or more blocked coronary arteries are bypassed using healthy blood vessels taken from another part of the body. These new vessels are grafted to the coronary arteries, enabling blood to detour around the blocked or damaged sections.
- Bypass creation: Surgeons create the bypass using veins or arteries from the patient’s legs (such as the saphenous vein), chest (internal mammary artery), or, less commonly, the arm.
- Restoring blood flow: This enables oxygen-rich blood to reach areas of the heart muscle previously deprived due to arterial blockages.
Why Might You Need Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Surgery?
CABG is typically recommended for people with significant blockages in their coronary arteries, especially when:
- Medications or lifestyle changes are not enough to relieve chest pain (angina).
- Multiple coronary arteries are narrowed or blocked.
- There is significant narrowing in the main coronary artery supplying blood to the left ventricle (the heart’s main pumping chamber).
- An earlier angioplasty or stenting procedure was not successful or feasible.
- Patients experience ongoing symptoms such as chest pain, or a high risk of heart attack is present.
Your cardiologist will help determine if CABG is appropriate based on your condition, symptoms, diagnostic findings, and overall health.
Conditions Commonly Treated with CABG
- Coronary artery disease (CAD)
- Heart failure associated with blocked arteries
- Life-threatening heart rhythm problems (arrhythmias) linked with CAD
- Refractory angina (persistent chest pain)
- Inadequate results or unsuitability for other interventions, such as angioplasty
- Multiple coronary blockages, often in diabetic patients
Preparation for Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Surgery
Your care team will guide you through important steps before surgery to ensure safety and optimal results:
- Preoperative tests: Includes blood work, chest X-rays, an ECG, and coronary angiography to plan the operation.
- Medication review: Some medications may need to be stopped or adjusted. Inform your care team about all drugs and supplements you are taking.
- Fasting: Generally, you will be advised not to eat or drink anything after midnight before the operation.
- Instructions: You will receive directions about bathing, shaving, and removing jewelry or nail polish before arriving at the hospital.
Discuss any questions or concerns with your surgeon and anesthesiologist prior to the procedure.
How Is Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Surgery Performed?
CABG is most often performed as an open-heart procedure, but minimally invasive techniques are possible in some cases. Here’s what to expect during the operation:
- Anesthesia: You will be under general anesthesia and completely asleep during surgery.
- Incision: The surgeon makes a large incision in the center of your chest and separates the breastbone (sternotomy) to access the heart. For minimally invasive or “keyhole” CABG, several small incisions are made, often utilizing special instruments and cameras.
- Harvesting blood vessels: A healthy vessel—typically the saphenous vein from the leg or the internal mammary artery from the chest—is carefully removed.
- Connection to heart-lung machine: In traditional CABG, your blood is circulated using a heart-lung bypass machine (cardiopulmonary bypass), allowing the heart to be stopped safely during the critical steps.
- Grafting the bypass: The harvested vessels are sewn above and below the blockages to reroute blood flow.
- Restarting the heart: The heart is restarted (sometimes with electric stimulation) and checked for healthy blood flow through the grafts. Temporary pacemaker wires may be attached, and drains are placed to remove excess fluid.
- Closing the chest: The sternum is closed with sturdy metal wires, and the incision is stitched or stapled shut with dissolvable sutures where possible.
The entire procedure typically takes 3 to 6 hours, depending on how many arteries need to be bypassed and individual patient factors.
Types of CABG Procedures
| Technique | Description |
|---|---|
| On-pump (Conventional) CABG | Heart is stopped and a heart-lung machine maintains blood flow and oxygenation during surgery. |
| Off-pump (Beating Heart) CABG | Heart continues to beat while the surgeon performs the bypass; suitable for certain patients. |
| Minimally Invasive / Keyhole | Performed through small chest incisions with special instruments and a camera. Not suited for every patient; may offer faster recovery. |
Risks and Complications of CABG Surgery
As with any major surgery, CABG carries some risks. Most procedures are successful, but potential complications can include:
- Bleeding and infection at the incision site
- Abnormal heart rhythms (arrhythmias), commonly atrial fibrillation
- Heart attack or stroke, though rare with careful patient selection
- Blood clots
- Memory issues or difficulty thinking clearly, often temporary
- Pneumonia or breathing problems
- Kidney dysfunction
Factors that can increase risk include advanced age, other health conditions (such as diabetes or chronic lung or kidney disease), and reduced heart function.
Recovery After Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Surgery
Most patients require several days in the hospital after CABG, starting in the intensive care unit (ICU) and moving to a standard ward before discharge. Post-surgical recovery can extend over weeks to months and involves:
- Monitoring in ICU for 1-2 days for vital signs, drainage tubes, IV medications, and oxygen support.
- Pain management and infection prevention.
- Gradual removal of tubes and monitoring devices as your condition stabilizes.
- Hospital discharge typically occurs after about a week, though some may need a longer stay.
- Prescribed medications to control pain, prevent infection, and manage heart function.
- Instructions for wound care and activity at home, including walking and gentle activities.
- Restrictions on heavy lifting and strenuous activity for 6–12 weeks during recovery.
- Cardiac rehabilitation to regain strength and fitness, usually supervised by healthcare professionals.
Full recovery may take several weeks. Follow all post-surgical advice closely and attend follow-up appointments for optimal recovery.
Long-Term Lifestyle and Prognosis
After CABG, adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle is vital to protect your heart and maintain the benefits of surgery:
- Eat a balanced diet low in saturated fats and cholesterol.
- Exercise regularly, as specified during cardiac rehabilitation.
- Quit smoking and avoid all tobacco products.
- Maintain a healthy body weight.
- Manage other conditions, such as hypertension, diabetes, and high cholesterol, with medications and lifestyle changes.
Your healthcare team will offer personalized recommendations to help prevent further heart problems.
Alternatives to Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Surgery
Depending on your health and the severity of arterial blockages, alternatives may include:
- Medications to control angina, high blood pressure, and cholesterol
- Percutaneous coronary intervention (angioplasty) and stenting
- Lifestyle changes such as diet, exercise, and quitting smoking
Some patients are candidates for less invasive approaches, while others may require CABG for best results. Your cardiology team will discuss suitable options for your condition.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the success rate of CABG surgery?
Coronary artery bypass grafts are highly successful, with most patients experiencing relief from symptoms and reduced risk of future heart attacks. Outcomes are best when patients follow their treatment and recovery plans closely.
How long will my hospital stay be after CABG?
Most patients remain in the hospital for 5 to 7 days after the operation, though this can vary based on individual recovery speed and any complications.
Can I live a normal life after bypass surgery?
With proper recovery, most people return to normal or near-normal activities within 6–12 weeks. Commitment to a heart-healthy lifestyle and regular check-ups is essential for long-term health.
What symptoms should prompt me to call my doctor after surgery?
Contact your care team if you experience fever, increasing pain, redness, swelling or oozing from incisions, rapid heartbeat, shortness of breath, chest pain, or swelling in your legs.
What can I do to improve my recovery?
Follow all post-surgical instructions, attend cardiac rehab, maintain a healthy diet, take medications as prescribed, and avoid tobacco.
Summary
Coronary artery bypass graft surgery is a life-saving and life-improving procedure for those with severe coronary artery disease. It can significantly reduce symptoms, lower the risk of heart attack, and improve quality of life. Adequate preparation, awareness of risks and benefits, diligent recovery, and proactive lifestyle changes are critical for the best outcome.
References
- https://www.nhs.uk/tests-and-treatments/coronary-artery-bypass-graft/how-its-done/
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kxc22Fjd1NQ
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK507836/
- https://www.yalemedicine.org/conditions/coronary-artery-bypass-grafting-cabg
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/16897-coronary-artery-bypass-surgery
- https://ctsurgery.weillcornell.org/surgical-services/cardiac-surgery/coronary-artery-bypass-graft-cabg
- https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/coronary-artery-bypass-grafting/during
Read full bio of Sneha Tete












