Understanding CIMT: Carotid Intima-Media Thickness Test Explained
Discover how CIMT testing uses ultrasound to assess your risk for heart disease and stroke in a painless, non-invasive procedure.
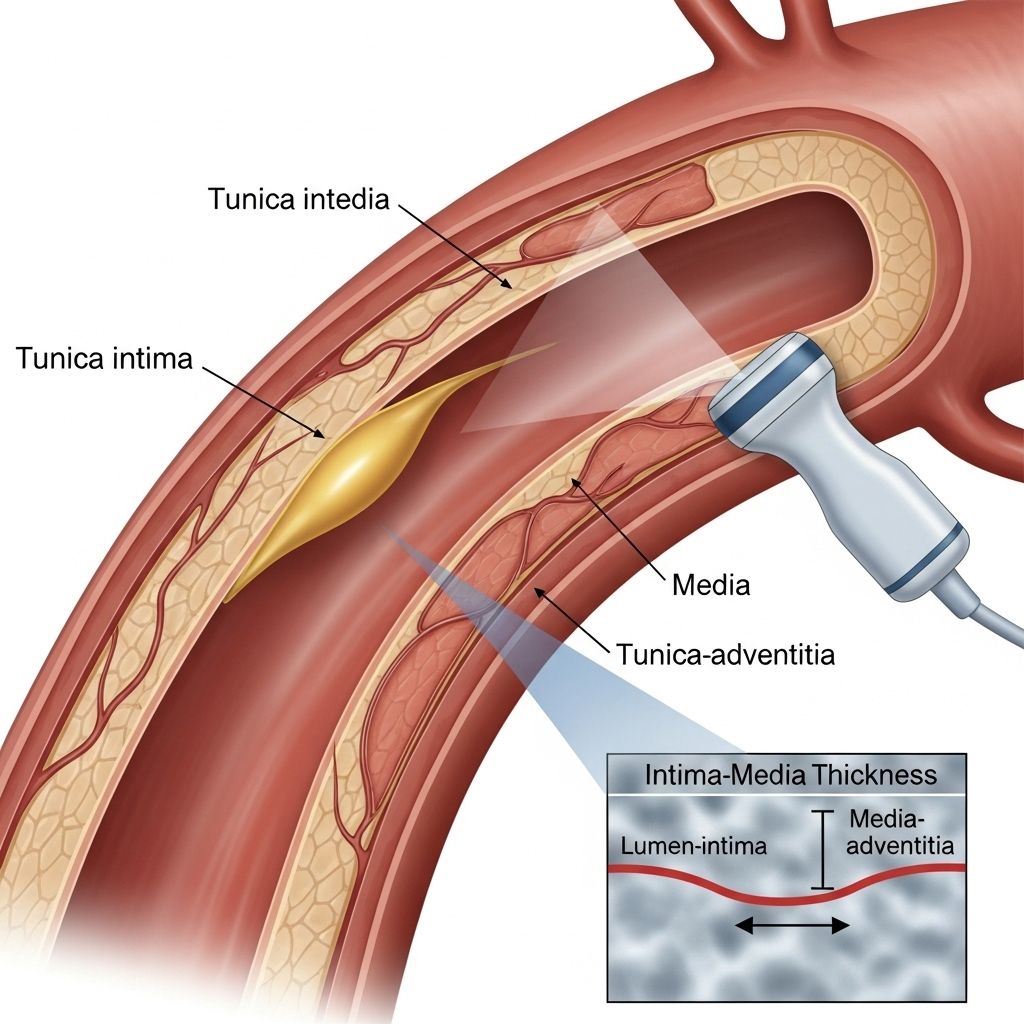
Carotid Intima-Media Thickness (CIMT) Test: What You Need to Know
The Carotid Intima-Media Thickness (CIMT) test is a modern, non-invasive screening method that helps identify early atherosclerosis—hardening and narrowing of the arteries—that can increase your risk of heart attack and stroke. Using advanced ultrasound technology, the CIMT test measures the thickness of the two inner layers of the carotid artery walls, providing valuable insights into arterial health even before traditional symptoms appear.
What Is the Carotid Intima-Media Thickness (CIMT) Test?
The CIMT test is a specialized type of vascular ultrasound designed to measure the thickness of the intima and media—the two innermost layers—of the carotid arteries. These arteries are key blood vessels in the neck that supply blood to your brain. An increase in the thickness of these layers is an early sign of atherosclerosis and can signal elevated risk for cardiovascular events, even when other tests are normal.
- Non-invasive and uses high-resolution ultrasound
- Measures carotid artery wall thickness (intima and media layers)
- Detects early arterial changes before symptoms develop
- Assesses risk for heart attack and stroke
Why Is CIMT Testing Done?
If you or your physician want a more precise understanding of your cardiovascular risk, CIMT testing provides clarity beyond conventional risk factor assessments such as cholesterol levels, blood pressure, and lifestyle habits. The main reasons for considering the test include:
- Early Detection: Identifies subclinical atherosclerosis before it progresses to more serious diseases
- Risk Stratification: Determines your risk for future cardiac events even if you’re asymptomatic
- Personalized Prevention: Helps tailor interventions and monitor response over time
This test is particularly recommended for individuals with:
- Family history of heart disease or stroke
- Multiple cardiovascular risk factors (such as smoking, diabetes, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, obesity, or an inactive lifestyle)
- Borderline or concerning cholesterol levels
- A desire for proactive cardiovascular risk assessment
How Does the CIMT Test Work?
The CIMT test employs a high-frequency ultrasound device—similar to those used in prenatal imaging—to capture live, detailed images of your carotid arteries. The steps typically include:
- A healthcare professional applies a special gel to your neck to improve sound wave transmission.
- An ultrasound probe (transducer) is gently moved against your skin along both sides of your neck where the carotid arteries lie.
- The device sends out and receives sound waves, creating images of the blood vessel walls on a computer monitor.
- The technician measures the thickness of the intima and media layers at standard points along each artery.
The entire procedure usually takes between 10–20 minutes for the scan itself, with a full appointment (including preparation and discussion) lasting about 30–45 minutes. The test is entirely painless and does not use radiation, needles, or contrast agents.
Preparing for the CIMT Test
One of the advantages of CIMT testing is its simplicity and minimal preparation requirements. Here’s what you need to know before your test:
- No fasting or blood draws required
- Wear loose, comfortable clothing, preferably with an open collar for easy access to your neck
- Remove any necklaces or jewelry
- No medications or special restrictions are typically necessary
Your provider will review your medical history, current medications, and may address any questions or concerns prior to the scan.
What Happens During the Test?
The CIMT scan is performed in a medical office or imaging center. Here’s what to expect:
- You’ll be asked to lie comfortably on your back, with your head turned slightly to the side.
- A technician applies ultrasound gel to your neck.
- The transducer is placed softly on your skin and moved along each side of your neck to capture images of both carotid arteries.
- You may hear quiet sounds from the ultrasound machine, but the procedure is silent and pain-free.
- After the ultrasound, the gel is wiped off, and you can return to non-strenuous activities immediately.
After the CIMT Test: Results and Interpretation
Once your CIMT scan is complete, the recorded images and thickness measurements are reviewed and interpreted by a qualified physician, often a cardiologist or radiologist. The key findings include:
- Carotid Intima-Media Thickness Value: Measured in millimeters; higher values generally reflect more advanced subclinical atherosclerosis
- Presence or Absence of Plaque: Any visible buildup indicates an increased risk for cardiac and cerebrovascular events
- Comparison to Age and Sex Norms: Your result is often compared to established reference ranges to contextualize your cardiovascular risk
You and your physician receive a detailed report, allowing for tailored recommendations. If your CIMT is increased, next steps may include:
- More aggressive management of cholesterol, blood pressure, or blood sugar
- Lifestyle changes: improved diet, increased physical activity, smoking cessation
- Follow-up CIMT scans to monitor improvement or progression
Benefits of the CIMT Test
The CIMT test offers unique advantages compared to traditional cardiovascular risk assessments alone. These benefits include:
- Early detection of atherosclerosis before symptoms appear
- Non-invasive and completely painless
- No exposure to ionizing radiation or contrast dyes
- Quick (typically completed within 20 minutes)
- Facilitates personalized risk reduction strategies
- Useful for ongoing monitoring of treatment effectiveness over time
Limitations and Risks of CIMT Testing
While CIMT is a valuable risk assessment tool, it does have limitations:
- Not a diagnostic tool for clinical disease; it indicates risk but does not confirm coronary artery blockage
- Less helpful in individuals with known vascular disease (prior heart attack or stroke)
- Insurance coverage is limited; often considered an out-of-pocket expense
- Not universally recommended for the general population; best for those at intermediate risk
Potential but rare risks include minor skin irritation from the gel or pressure, but the procedure overall is extremely safe for almost all patients.
Who Should Consider CIMT Testing?
CIMT testing is most appropriate for the following groups:
- Adults aged 40–70 with one or more risk factors (family history, hypertension, diabetes, high cholesterol, smoking, obesity)
- Individuals with intermediate or uncertain risk after standard risk scoring
- Patients interested in proactive cardiovascular screening
It is not recommended for people who:
- Already have diagnosed coronary artery disease, a history of heart attack, revascularization procedures, stroke, or significant peripheral arterial disease
CIMT Thickness: Reference Values and Interpretation
| CIMT Value (mm) | Risk Category | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Below 0.6 | Low | Arteries show minimal thickening; low risk of atherosclerosis |
| 0.6 – 0.9 | Average | Expected range for age; continue cardiovascular risk management as appropriate |
| Above 0.9 | High | Suggests increased аtherosclerosis; intensify monitoring and risk reduction strategies |
Note: Normal ranges can vary depending on age, sex, and local lab standards. Always discuss results with your healthcare provider.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about CIMT Testing
What does CIMT stand for?
CIMT stands for Carotid Intima-Media Thickness, referring to the ultrasound measurement of the inner two layers of the carotid artery wall.
Is the CIMT test painful or risky?
No, the CIMT test is completely painless, safe, and non-invasive. It uses ultrasound and has no radiation exposure or significant risks.
How long does the CIMT test take?
The scan itself usually takes between 10–20 minutes. Including preparation and discussion, your total visit may last up to 45 minutes.
Do I need to prepare beforehand?
No special preparation or fasting is needed. Wear loose, comfortable clothing and remove any jewelry around your neck.
Will insurance cover CIMT testing?
CIMT is often not covered by standard insurance policies in many locations. Check with your provider to confirm costs prior to scheduling.
Can CIMT detect blockages in arteries?
CIMT does not detect acute blockages but measures wall thickening, which is a marker of early atherosclerosis and future risk, not current obstruction.
Who should avoid CIMT testing?
People with a history of major cardiovascular events (heart attack, bypass, stents, stroke) or known artery disease may not benefit from CIMT, as their risk is already established.
Takeaway: The Role of CIMT in Heart and Stroke Prevention
The Carotid Intima-Media Thickness (CIMT) test offers cutting-edge, non-invasive insights into your arterial health and risk of future cardiovascular disease. By identifying early thickening of the carotid artery walls, you and your healthcare provider can personalize your prevention strategies for heart attack and stroke.
If you have one or more risk factors but no symptoms or prior vascular disease, talk to your doctor about whether CIMT is right for you. As with all health decisions, use the results in combination with clinical evaluation and risk factor management for the best protection of your heart and brain health.
References
- https://www.nexushealthspan.com/blog/what-is-the-typical-procedure-and-duration-for-cimt-testing-at-clinics-in-orange-county
- https://www.radiologyinfo.org/en/info/carotid-intima
- https://www.mpcp.com/articles/preventative-care/new-test-identifies-heart-stroke-risk-earlier/
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC12162042/
- https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/JAHA.123.031217
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6055970/
- https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/STROKEAHA.118.024692?doi=10.1161%2FSTROKEAHA.118.024692
Read full bio of Sneha Tete












