16:8 Intermittent Fasting: Health Benefits, How It Works, and Tips
Discover the science-backed benefits, practical guidance, and essential tips for adopting the popular 16:8 intermittent fasting plan.
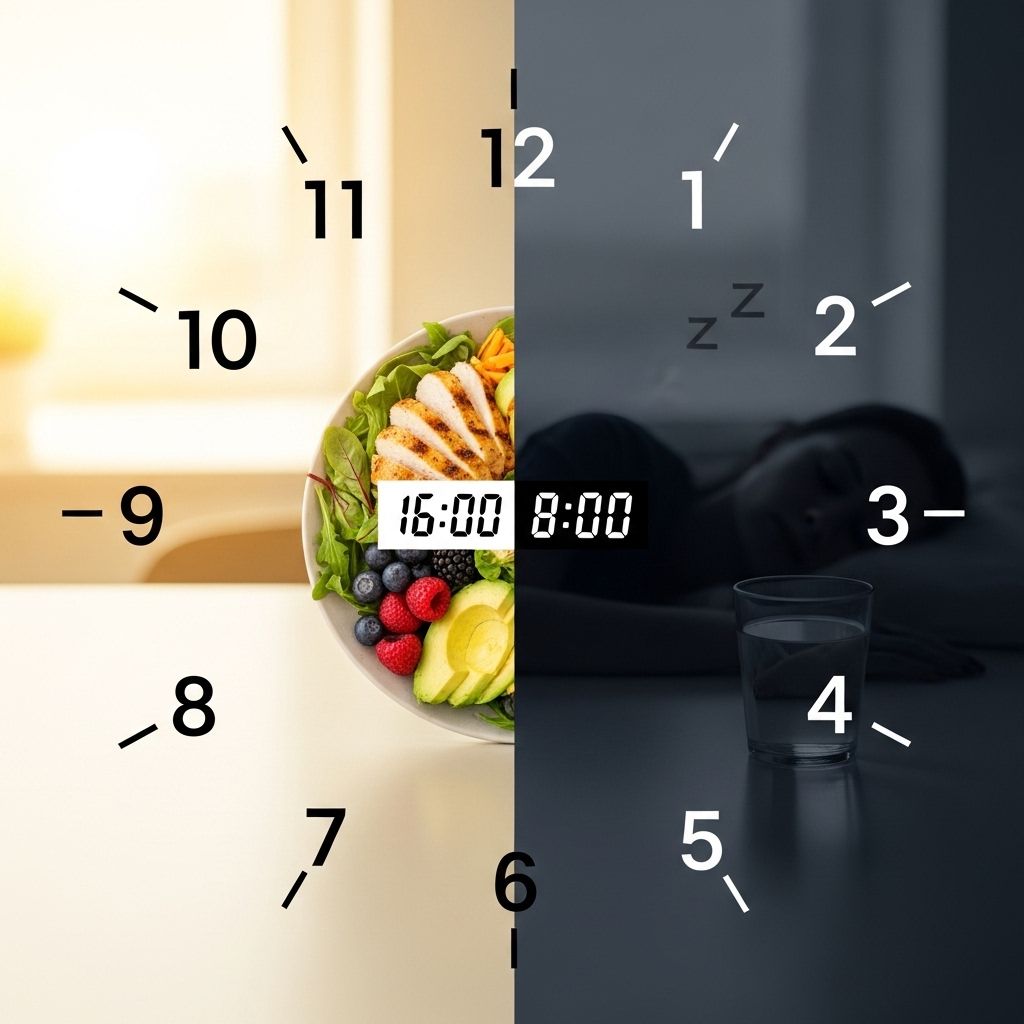
16:8 Intermittent Fasting: A Comprehensive Guide to Its Benefits and How to Succeed
Intermittent fasting (IF) has gained substantial popularity as an approach to weight management and overall health improvement. Among the various fasting schedules, the 16:8 method has emerged as one of the most widely adopted styles for its flexibility, simplicity, and science-backed benefits. This article offers a thorough breakdown of the 16:8 plan: what it is, how it works, its health advantages, tips and potential drawbacks, recommended foods, and answers to common questions.
Table of Contents
- What Is 16:8 Intermittent Fasting?
- How to Get Started With 16:8 Fasting
- Top Health Benefits of the 16:8 Diet
- Drawbacks and Considerations
- Best Foods for 16:8 Fasting
- Tips for Successful 16:8 Fasting
- Frequently Asked Questions
What Is 16:8 Intermittent Fasting?
The 16:8 intermittent fasting protocol involves restricting all food and calorie-containing beverage intake to a set 8-hour window each day. During the remaining 16 hours, only water, tea, or other no-calorie drinks are permitted. This cyclical pattern typically repeats daily, but some people opt for fewer fasting days per week, depending on their preferences and lifestyle.
- Popular eating windows: Noon to 8 p.m., 9 a.m. to 5 p.m., 10 a.m. to 6 p.m., 7 a.m. to 3 p.m.
- Most participants start by simply skipping breakfast and consume their meals between lunch and dinner.
- It’s vital to select the 8-hour period that best fits your schedule, energy levels, and lifestyle.
How to Get Started With 16:8 Fasting
Beginning a 16:8 fasting routine is straightforward but requires basic planning and flexibility. Here is a step-by-step approach:
- Pick your fasting window: Choose an 8-hour span during the day when you feel you have most control over your food choices and social activities.
- Set reminders: Use alarms or smartphone apps to help manage your eating and fasting periods.
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water, herbal tea, or black coffee throughout your 16-hour fast.
- Plan balanced meals and snacks: Focus on nutrient-rich foods during your eating window for optimal results.
- Adjust gradually: If you’re new to fasting, start with shorter fasts (try 12:12 or 14:10) and work towards 16:8 as your body accommodates.
Top Health Benefits of the 16:8 Diet
While weight loss is the most immediate appeal for many, the 16:8 diet offers a range of other health advantages. Here’s what research and expert commentary reveal:
- Weight Loss & Fat Reduction: Limiting meals to an 8-hour window typically results in eating fewer calories overall, which, when coupled with healthy food choices, may help reduce body fat.
- Blood Sugar Control: Fasting periods can improve insulin sensitivity and help regulate blood glucose levels, making 16:8 a promising strategy for supporting metabolic health and prediabetes management.
- Simplicity & Sustainability: The absence of strict rules around what to eat, combined with a focus on when to eat, makes 16:8 easier to maintain compared to many calorie-restrictive diets.
- Reduced Cravings and Mindless Snacking: Structured eating times often curb unplanned snacking, which can improve dietary quality and calorie control.
- Potential Longevity Benefits: Fasting has been linked in several studies to improved cellular health, reduced inflammation, and slowed aging processes, although further human research is needed.
- Improved Digestion: Extended overnight fasting can support digestive health and reduce feelings of bloating for many people.
| Eating Window | Who It Suits |
|---|---|
| 12 p.m. – 8 p.m. | Night owls, those who prefer dinner with family/friends |
| 9 a.m. – 5 p.m. | Early risers, breakfast fans with lighter dinners |
| 10 a.m. – 6 p.m. | Balanced approach for mid-morning energy and early evening meals |
| 7 a.m. – 3 p.m. | Maximizes fasting time during evening and sleep hours |
Drawbacks and Things to Consider
Despite its advantages, 16:8 intermittent fasting isn’t universally suitable. Potential issues include:
- Initial hunger and mood swings: Especially in the first week, you may feel irritable, tired, or distracted between meals.
- Potential nutrient gaps: If eating windows are rushed or meals lack variety, vital nutrients may be missed.
- May not suit everyone: Those with advanced diabetes, eating disorders, pregnant/nursing women, or those with certain medical conditions should consult a doctor before trying any fasting program.
- Risk of Overeating: Compensating during eating windows with excessively large or unhealthy meals can undermine potential benefits.
- Possible social obstacles: Social mealtimes, late-night events, or irregular schedules may need special planning.
Best Foods to Eat During Your 8-Hour Window
Maximizing health benefits with 16:8 fasting requires thoughtful meal planning:
- Lean Proteins: Chicken, fish, eggs, tofu, and legumes support fullness and muscle maintenance.
- Whole Grains: Brown rice, oats, quinoa, and whole wheat bread provide sustained energy.
- Healthy Fats: Avocado, nuts, olive oil, and seeds nourish your body and help you feel satisfied.
- Plenty of Vegetables: Leafy greens, cruciferous veggies, and colorful produce boost fiber, minerals, and antioxidants.
- Moderate Fruits: Focus on berries, apples, citrus, and bananas for natural sweetness and nutrients.
- Hydration: Water, herbal tea, and black coffee (no sugar or cream) keep you hydrated between meals.
Foods to limit: Sugary beverages, fried foods, highly processed snacks, and refined grains can reduce results and spike hunger.
Tips for Successful 16:8 Intermittent Fasting
- Start slow: Ease in by shortening your fasting period and gradually adjusting as you become comfortable.
- Prioritize whole foods: Nutrient-rich, unprocessed foods help prevent energy slumps and cravings during the fast.
- Stay hydrated: Water, herbal tea, and coffee are your allies during fasting hours.
- Listen to your body: Mild hunger is normal. If you feel faint, excessively tired, or unwell, break your fast and consult an expert.
- Monitor progress: Keep a journal or app to track feelings, meals, and metrics such as body weight or blood sugar if relevant.
- Don’t obsess over calories: Balance and consistency matter more than rigid calorie counting, but avoid significant overeating during your window.
- Adjust as needed: Lifestyle changes, special occasions, or travel may require shifting your schedule.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Can I drink coffee or tea during the fasting phase?
A: Yes, water, plain coffee, and unsweetened tea are allowed. Avoid adding sweeteners, cream, or milk, as these break the fast.
Q: Does skipping breakfast affect my metabolism?
A: Research shows that intermittent fasting does not slow metabolism; in fact, it may boost metabolic efficiency for many people.
Q: Can I exercise on a 16:8 fasting schedule?
A: Light to moderate activity is usually well-tolerated during fasting. For strenuous workouts, some people prefer exercising during their eating window.
Q: Will I experience hunger?
A: Mild hunger is common at first but often declines as your body adapts. Eating protein and fiber-rich meals during your eating window can help manage hunger.
Q: Is 16:8 fasting safe for everyone?
A: It is generally safe for healthy adults, but those with chronic conditions, underweight, pregnant, or breastfeeding should consult a healthcare provider before starting.
Sample 16:8 Fasting Meal Plan
| Time | Meal |
|---|---|
| 12:00 p.m. | Grilled chicken salad with dark greens, tomatoes, olive oil dressing; side of brown rice |
| 3:00 p.m. | Apple with almond butter or low-fat greek yogurt and berries |
| 6:00 p.m. | Baked salmon with quinoa, steamed broccoli, and roasted carrots |
| 7:30 p.m. | Small handful of nuts or a boiled egg |
Expert Insights on the 16:8 Diet
Medical professionals generally regard 16:8 fasting as a safe and evidence-based option for most healthy adults seeking gradual, sustainable weight management and enhanced metabolic health. Unlike extreme diets, its flexibility allows for personalization, which improves adherence. Experts and nutritionists recommend focusing on whole foods and remaining attentive to hydration—particularly during fasting hours.
The Bottom Line
The 16:8 method of intermittent fasting provides a straightforward framework for improving health, supporting weight loss, and stabilizing blood sugar. Its simplicity makes it easily adaptable for most people, but its effectiveness depends on balanced nutrition and consistent execution. Consult with your health provider if you have underlying health conditions or specific dietary needs before beginning any fasting regimen.
References
- https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/16-8-intermittent-fasting
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-hSERcBUsGY
- https://www.health.harvard.edu/staying-healthy/can-intermittent-fasting-help-with-weight-loss
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/nutrition-and-healthy-eating/expert-answers/intermittent-fasting/faq-20441303
- https://health.clevelandclinic.org/intermittent-fasting-4-different-types-explained
- https://www.massgeneralbrigham.org/en/about/newsroom/articles/pros-and-cons-of-intermittent-fasting
Read full bio of Sneha Tete












