Comprehensive Remedies for Canker Sores: Relief, Healing, and Prevention Strategies
Explore effective remedies, expert advice, and prevention tips for canker sores to help you heal faster and minimize recurrence.
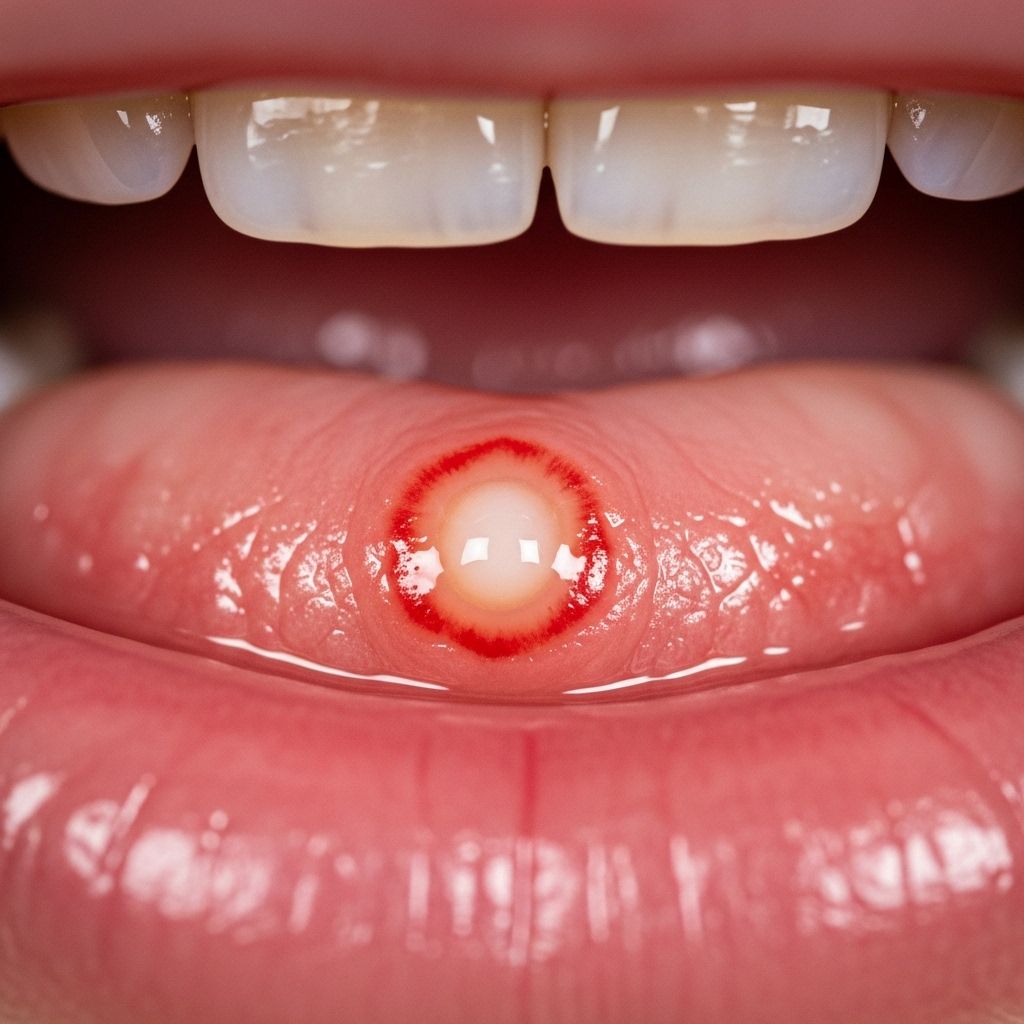
Canker sores, also known as aphthous ulcers, are painful lesions that occur inside the mouth, typically on the inner cheeks, lips, tongue, or gums. Although they are not contagious and usually heal on their own, their discomfort and recurrence can disrupt everyday life. This guide explores extensive remedies, from home treatments and over-the-counter options to medical interventions, expert advice, and lifestyle strategies for both relief and prevention.
Table of Contents
- Overview: Understanding Canker Sores
- Symptoms and Types of Canker Sores
- What Causes Canker Sores?
- How Long Do Canker Sores Last?
- Effective Home Remedies for Canker Sores
- Over-the-Counter and Prescription Treatments
- Lifestyle Modifications & Prevention Tips
- When to Seek Medical Help
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Overview: Understanding Canker Sores
Canker sores are small, shallow ulcers that appear in the soft tissues of your mouth or at the base of your gums. Unlike cold sores, they do not occur on the surface of your lips and aren’t caused by viruses. Canker sores often make eating, drinking, and even talking uncomfortable, although they generally resolve on their own within one to two weeks.
Symptoms and Types of Canker Sores
- Minor canker sores: Small, round or oval, white or yellow ulcers with a red border; usually heal within 2 weeks without scarring.
- Major canker sores: Larger, deeper ulcers; may last up to 6 weeks and potentially leave scars.
- Herpetiform canker sores: Tiny, multiple clusters that may merge into one large ulcer; usually heal in about 2 weeks.
Typical symptoms include burning or tingling sensations before sores appear, pain during eating or talking, and visible lesions inside the mouth.
What Causes Canker Sores?
The exact cause of canker sores remains unclear, but several triggers and risk factors are recognized:
- Minor injuries to oral tissues (e.g., biting your cheek, dental work)
- Food sensitivities (e.g., acidic or spicy foods)
- Vitamin deficiencies (e.g., B12, folate, iron, zinc)
- Hormonal changes (e.g., menstruation)
- Stress and emotional disturbances
- Underlying medical conditions (e.g., autoimmune disorders, gluten sensitivity)
How Long Do Canker Sores Last?
Most canker sores heal without treatment within one to two weeks for minor sores; major or herpetiform types may take longer. If healing is delayed or symptoms are severe, consult a healthcare provider.
Effective Home Remedies for Canker Sores
Many canker sore remedies can be found at home. These options may not cure sores overnight but can help decrease pain, speed up healing, and reduce inflammation:
Salt Water Rinse
- Mix 1 teaspoon of salt with 1 cup of warm water.
- Swish in your mouth for 30 seconds, then spit.
- Repeat several times daily to clean the sore and encourage healing.
Baking Soda Paste
- Combine equal parts baking soda and water to form a paste.
- Apply directly to the sore for neutralization of acids and reduction of inflammation.
Honey
- Known for its antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties.
- Apply a small amount directly to the sore to soothe pain and possibly speed healing.
Aloe Vera
- Soothes inflammation and promotes healing.
- Apply fresh aloe vera gel or juice directly onto the sore or rinse your mouth with aloe vera juice.
Coconut Oil
- Has antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effects.
- Apply liberally to the sore, several times a day.
Hydrogen Peroxide (Diluted)
- Use a 3% solution diluted with water (equal parts).
- Apply gently with a cotton swab to the sore or use as a mouth rinse briefly.
Milk of Magnesia
- Magnesium hydroxide neutralizes acids and coats the sore for pain relief.
- Apply a small amount multiple times daily.
Ice Chips
- Sucking on ice chips can help temporarily numb the area and alleviate pain.
Chamomile Tea Compress
- Chamomile has anti-inflammatory properties.
- Apply a cooled chamomile tea bag directly to the affected area for soothing relief.
Yogurt (with live cultures)
- May help balance oral bacteria and promote healing.
Summary Table: Home Remedy Comparison
| Remedy | Main Benefit | Ease of Use |
|---|---|---|
| Salt Water Rinse | Cleans sore, reduces swelling | Very easy |
| Baking Soda Paste | Neutralizes acid, reduces inflammation | Easy |
| Honey | Antibacterial, soothes pain | Very easy |
| Aloe Vera | Speeds healing, reduces pain | Easy |
| Coconut Oil | Antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory | Easy |
| Hydrogen Peroxide | Cleans, reduces bacteria | Moderate |
Over-the-Counter and Prescription Treatments
If home remedies aren’t sufficient for pain relief or healing, various products are available over-the-counter and by prescription:
Topical Anesthetics
- Lidocaine gel or cream: Numbs pain and reduces inflammation.
- Benzocaine gels: Offer quick, temporary numbness.
Topical Corticosteroids
- Hydrocortisone ointment: Reduces inflammation and promotes healing.
- Prescription gels: May contain stronger steroids for severe or persistent sores.
Mouth Rinses
- Chlorhexidine gluconate: Antiseptic mouthwashes clean and help prevent secondary infections.
- Lidocaine-based rinses: Prescription or OTC versions are used for pain relief.
- Corticosteroid rinses: Sometimes prescribed for multiple or severe sores.
NSAIDs & Pain Relievers
- Diclofenac-containing gels: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medication for topical pain relief.
Protective Pastes and Film-Forming Agents
- Oral adhesive pastes: Form a barrier over the sore, shielding it from irritation and aiding comfort while eating or drinking.
- Liquids with film-forming agents: Similar effect to pastes, can protect and soothe.
Summary Table: OTC & Prescription Remedies
| Type | Examples | Main Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Anesthetic Gel | Lidocaine, Benzocaine | Pain relief |
| Corticosteroid | Hydrocortisone ointment | Anti-inflammatory |
| Antiseptic Rinse | Chlorhexidine | Clean, prevent infection |
| Protective Paste | Oral adhesive | Barrier, comfort |
Lifestyle Modifications & Prevention Tips
Good oral hygiene and healthy lifestyle habits can reduce the risk of recurrent canker sores and support faster healing:
- Brush and floss regularly; avoid irritating the gums and cheeks.
- Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and gentle, non-abrasive toothpaste.
- Avoid foods that trigger or worsen sores (e.g., acidic, spicy, or sharp foods).
- Maintain balanced nutrition; address vitamin or mineral deficiencies (B12, iron, folate, zinc).
- Stay hydrated for mucosal health.
- Practice stress management: Yoga, meditation, or deep breathing can reduce frequency in stress-related outbreaks.
When to Seek Medical Help
- If sores are unusually large, last more than two weeks, or are accompanied by fever or other concerning symptoms, consult a healthcare provider.
- See a dentist if normal remedies do not produce results, or if canker sores recur frequently and severely.
- Professional evaluation may be needed to rule out underlying health issues or prescribe advanced therapies.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: Are canker sores contagious?
No, canker sores are not contagious, unlike cold sores.
Q2: What foods should I avoid if I have a canker sore?
Stay away from spicy, acidic, salty, or rough-textured foods that can irritate the ulcer.
Q3: Can stress cause canker sores?
Yes, stress is a recognized trigger and managing it may help prevent outbreaks.
Q4: What’s the fastest way to get rid of a canker sore?
While no remedy cures canker sores immediately, combining topical anesthetics, mouth rinses, and gentle home care can help speed up recovery.
Q5: Should I worry about recurrent canker sores?
Often, repeated sores are mild and may be related to triggers like stress or diet. However, frequent/severe outbreaks should be medically assessed.
Additional Information & Expert Tips
- Canker sores affecting children should be approached with safe, age-appropriate remedies; always consult a pediatrician.
- If pain is intense or interfering with eating/drinking, ask your provider for prescription-strength treatments.
- Track triggers in a journal to help identify causes of recurrent sores (e.g., stress events, specific foods).
- Sometimes, switching toothpaste to an SLS-free (sodium lauryl sulfate-free) product can reduce outbreak frequency.
Conclusion
Canker sores may be common and troublesome, but multiple relief options exist. Combine home treatments with OTC products for symptom relief, maintain excellent oral hygiene, and adjust your diet and stress levels to minimize recurrence. Consult your dental or medical provider for persistent, severe, or concerning cases to ensure timely diagnosis and advanced care.
References
- https://www.healthline.com/health/dental-and-oral-health/how-to-get-rid-of-canker-sores
- https://www.centraldavisdental.com/2024/11/04/canker-sores-the-best-tips/
- https://www.inglewoodfamilydental.ca/treatment-for-canker-sores-on-gums/
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/10945-canker-sores
- https://www.walgreens.com/q/canker+sore+relief
- https://maaom.memberclicks.net/index.php%3Foption=com_content&view=article&id=86:canker-sores-treatment&catid=22:patient-condition-information&Itemid=120
- https://ufhealth.org/conditions-and-treatments/canker-sore
- https://kidshealth.org/en/teens/canker.html
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK546251/
Read full bio of Sneha Tete











