Gum Boil Remedies: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Treatments
Discover practical ways to relieve oral abscess pain and prevent recurring infections.
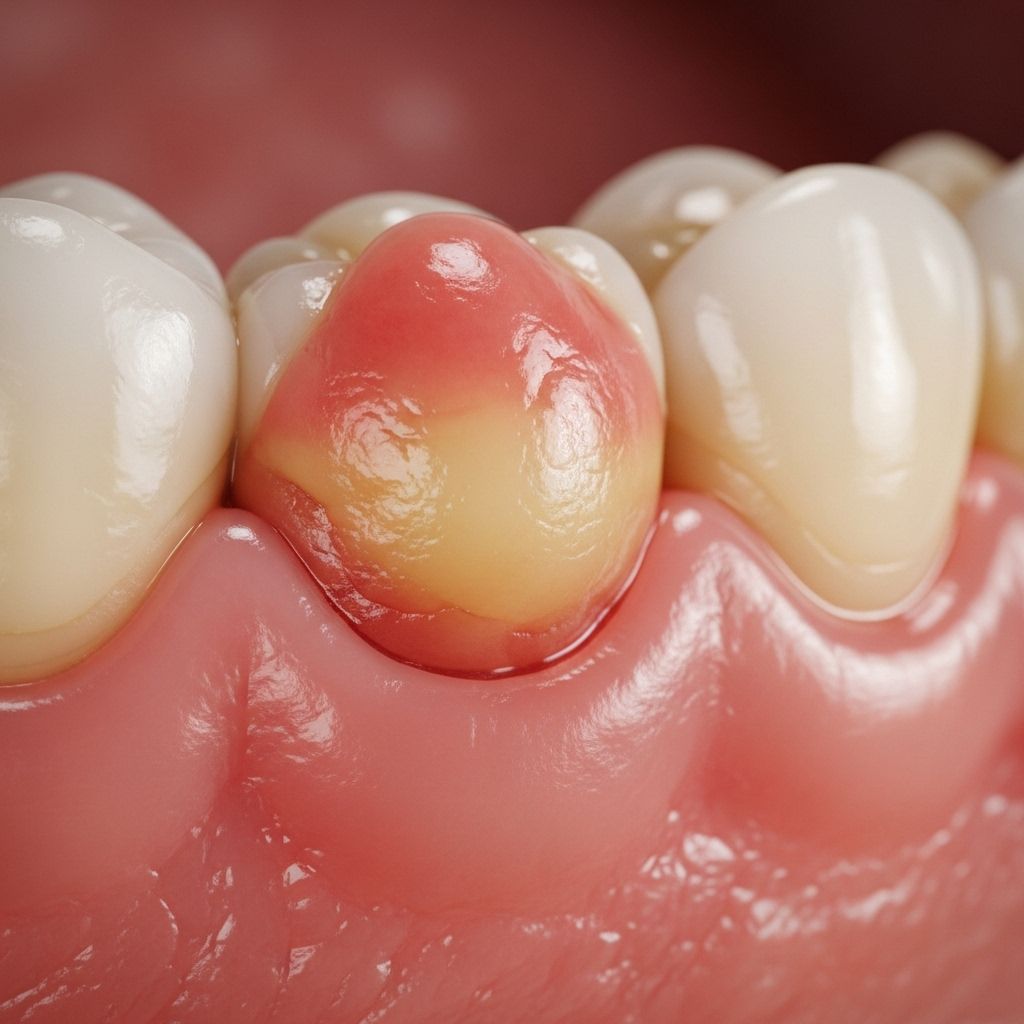
Gum boils, also known as gum abscesses or parulis, are painful and unsightly oral concerns that can indicate underlying dental issues. These pus-filled bumps not only affect daily activities like eating and speaking but may, if untreated, lead to serious health complications. Understanding gum boils—including their causes, symptoms, home remedies, and treatment options—is essential to maintaining optimal oral health and preventing further problems.
In This Article
- What Is A Gum Boil?
- Causes of Gum Boils
- Symptoms of Gum Boils
- What Does a Gum Boil Look Like?
- Home Remedies for Gum Boil Relief
- Professional Treatment Options
- Potential Complications
- Prevention Tips
- Frequently Asked Questions
What Is A Gum Boil?
A gum boil refers to a swollen, pus-filled bump forming on the gums due to bacterial infection. Medically termed as a parulis or gum abscess, boils develop when bacteria collect inside the tissues—either at the gum line, around the root of a tooth, or deeper in the supporting gum tissues. These infections often result from food debris, dental decay, or untreated gum disease and require prompt attention to avoid worsening complications.
Types of Gum Boils
| Type | Description | Location |
|---|---|---|
| Periodontal Abscess | Pus collection within the gum tissue; most common type | Periodontal pocket (deep gum tissue) |
| Periapical Abscess | Pus accumulates near the tooth’s root | Tip of the tooth’s root |
| Gingival Abscess | Pus builds up in the gum line | Visible edge of gums |
Causes of Gum Boils
Understanding what leads to gum boils helps ensure proper treatment and prevention. Several factors can trigger these painful abscesses:
- Poor oral hygiene (leading to plaque buildup)
- Gum diseases: Gingivitis and periodontitis
- Tooth decay or infected teeth
- Food debris lodged in the gums
- Dental procedures: Extractions, root canals
- Trauma or injury to gums
- Impacted teeth or erupted wisdom teeth
- Overall weak immunity
- Tobacco use
- Bacterial infection (especially gram-negative anaerobic bacteria)
- Pre-existing chronic diseases (that lower resistance to infection)
If not addressed early, these causes can intensify gum inflammation and promote abscess development.
Symptoms of Gum Boils
Gum boils often start with localized discomfort and can quickly progress. Look for the following signs:
- Localized pain in the gums
- Swollen, tender bump—often red or inflamed
- Pus discharge (may taste foul)
- Bad breath
- Earache (if infection spreads)
- Bleeding gums
- Sensitivity to hot or cold foods
- Swelling in surrounding gum tissue
- Nausea and low-grade fever (in severe cases)
Persistent pain, fever, or pus draining from the boil can indicate a more serious infection and warrants the attention of a dental professional.
What Does a Gum Boil Look Like?
A gum boil typically appears as a swollen, red, pus-filled lump on the gums, usually neighboring a tooth. It can range from the size of a small pimple to a larger, more prominent swelling. These bumps are generally tender to the touch and may rupture, releasing pus and causing further discomfort.
Home Remedies for Gum Boil Relief
The following home care strategies can help relieve the symptoms of gum boils. While professional dental care is necessary to address underlying causes, these remedies may provide temporary relief and help reduce recurrence risk:
- Good Oral Hygiene
- Brush twice daily using a soft-bristled toothbrush.
- Floss regularly to remove food debris and plaque between teeth.
- Use an antibacterial mouthwash to minimize oral bacteria.
- Saltwater Rinse
- Mix 1 teaspoon of salt in a glass of warm water.
- Rinse your mouth for 30-60 seconds, three to four times daily.
- Reduces inflammation and helps draw out pus.
- Essential Oils
- Tea tree, clove, and peppermint oils have antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effects.
- Mix a few drops with coconut oil and gently apply to affected gum tissue.
- Always dilute and perform a patch test before use.
- Warm Compresses
- Apply a clean, warm compress externally to the cheek over the boil area. This helps reduce pain and swelling.
- Turmeric Paste
- Mix turmeric powder with water to create a paste.
- Apply gently to the gum boil for its natural anti-inflammatory benefits.
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relief
- Ibuprofen or acetaminophen may help alleviate pain and inflammation.
- Follow recommended dosage and consult your healthcare provider if needed.
Note: Home remedies should be considered supportive—visit your dentist if symptoms persist or worsen, or if you notice fever or swelling extending beyond the gums.
Professional Treatment Options
If gum boils do not improve with home care or if symptoms intensify, seek immediate professional dental treatment. Common interventions include:
- Drainage of the abscess by a dentist
- Antibiotic therapy (e.g., amoxicillin, metronidazole, azithromycin, cefixime, penicillin)
- Root canal therapy for infections involving tooth roots
- Extraction of irreversibly damaged or infected teeth
- Deep cleaning of gum pockets (scaling and root planing)
Timely professional care not only resolves infections but also prevents recurrence, tooth loss, or spread to other areas of the body.
Potential Complications
Ignoring or inadequately treating gum boils may result in severe complications, including:
- Spread of infection to surrounding tissues, jawbone, or bloodstream (septicemia)
- Shock (from severe, uncontrolled infection)
- Tooth loss
- Oral cancer cell formation (rarely, from recurrent untreated abscesses)
- Systemic health risks for those with compromised immunity
Early recognition and management are crucial to avoid these risks.
Prevention Tips
Incorporate these habits into your routine to minimize the likelihood of gum boils:
- Brush and floss daily using proper technique
- Limit sugary foods and beverages that trigger bacterial growth
- Schedule regular dental checkups and cleanings
- Avoid tobacco products
- Address dental problems (decay, fillings, crowded teeth) promptly
- Strengthen immunity with nutritious foods, hydration, and stress management
These preventive strategies significantly reduce the risk of gum infections and related complications.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can stress cause gum boils?
Stress can compromise the immune system, diminishing its ability to fight off infections that cause gum boils.
What antibiotics treat gum boils?
Commonly prescribed antibiotics for gum boil treatment include amoxicillin, metronidazole, azithromycin, cefixime, and penicillin. A dentist will select the most appropriate medication based on the infection’s severity and bacterial type.
Are gum boils contagious?
Gum boils themselves are not contagious, but the underlying infection can spread locally within the mouth if left untreated.
Will a gum boil go away on its own?
A minor gum boil may rupture and drain, temporarily reducing symptoms, but the underlying cause (infection or dental issue) will persist until properly treated.
When should I see a dentist?
Seek professional advice if you notice persistent pain, swelling, fever, pus discharge, or if home remedies provide no improvement within a few days.
To Sum It Up
Gum boils signal an active infection in the gum tissue, often due to poor oral hygiene, dental disease, or trauma. Practicing sound oral care habits, recognizing early symptoms, and utilizing proven home remedies can help alleviate discomfort and minimize infections. However, professional dental treatment remains the definitive solution to resolve underlying problems and prevent the potentially severe consequences of untreated gum boils.
References
- https://www.healthline.com/health/gum-boils
- https://www.stylecraze.com/articles/gum-boil/
- https://chrysanth.london/2024/11/29/10-proven-gum-boil-treatments-you-can-try-at-home/
- https://www.stylecraze.com/author/sanchari_bhattacharya/
- https://pratima12.rssing.com/chan-73058334/all_p70.html
- https://www.coursehero.com/file/55917194/IPIL-IPILdocx/
Read full bio of medha deb












