Eustachian Tube Dysfunction Remedies: Complete Treatment Guide
Comprehensive solutions for ear pressure, pain, and hearing problems
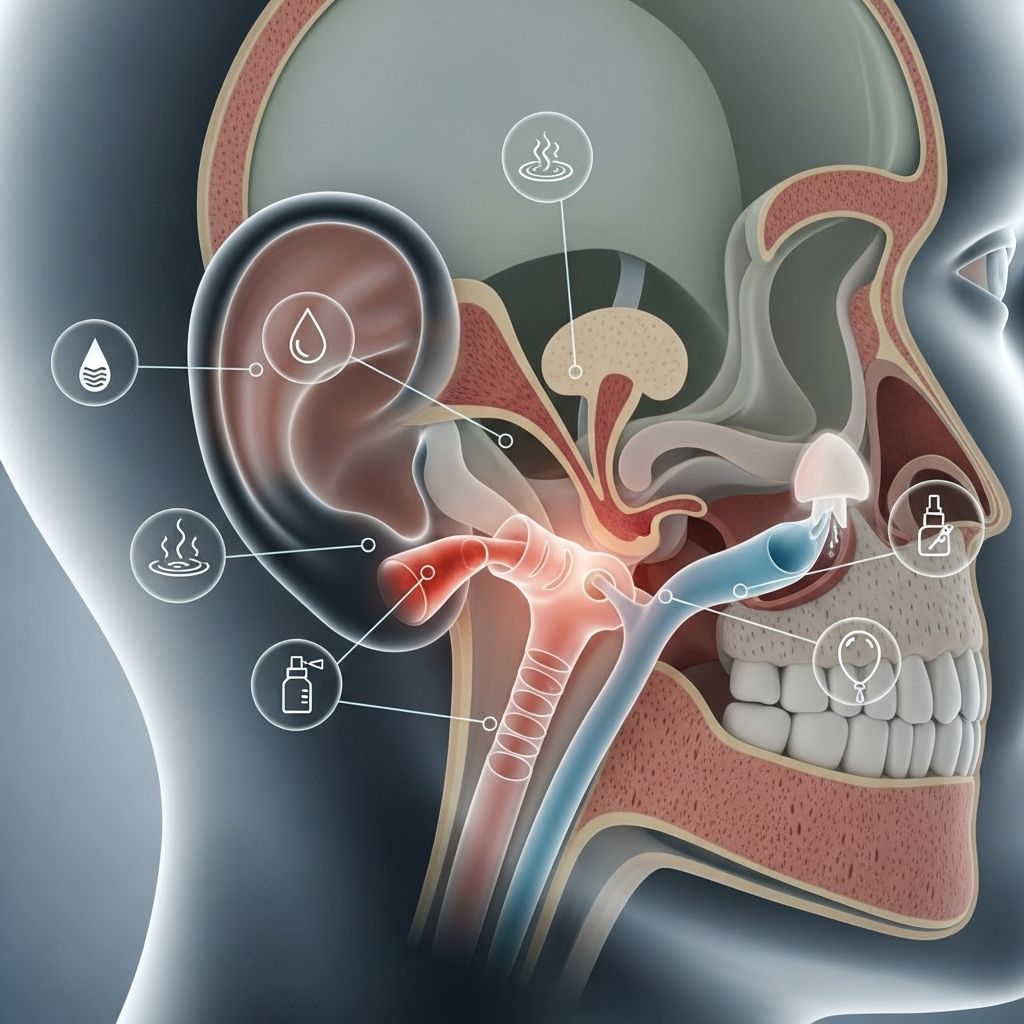
Eustachian tube dysfunction (ETD) affects millions of people worldwide, causing uncomfortable symptoms like ear pressure, muffled hearing, and pain. The eustachian tubes are small passageways connecting your throat to your middle ear, responsible for equalizing air pressure and draining fluid. When these tubes become blocked or fail to function properly, it can lead to significant discomfort and hearing issues.
Understanding effective remedies for eustachian tube dysfunction is crucial for managing symptoms and preventing complications. This comprehensive guide explores various treatment options, from simple home remedies you can try immediately to medical interventions that may be necessary for severe cases.
Understanding Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
Eustachian tube dysfunction occurs when the small tubes connecting your middle ear to the back of your throat fail to open and close properly. These tubes normally open when you swallow, yawn, or sneeze, allowing air to flow in and out while maintaining equal pressure on both sides of your eardrum.
When the eustachian tubes become blocked, swollen, or fail to function correctly, it creates an imbalance in pressure that leads to uncomfortable symptoms. The condition can be acute, lasting just a few days, or chronic, persisting for weeks or months.
Common Symptoms
The symptoms of eustachian tube dysfunction can vary in severity and may include:
- Feeling of fullness or pressure in the ears
- Muffled or dulled hearing
- Popping or clicking sensations in the ear
- Mild to moderate ear pain
- Tinnitus (ringing or buzzing in the ears)
- Difficulty maintaining balance
- Worsening symptoms with altitude changes
Primary Causes of Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
Understanding the underlying causes of ETD is essential for choosing the most effective remedies. The most common causes include:
Respiratory Infections
The most frequent cause of eustachian tube dysfunction is upper respiratory infections, including the common cold and flu. These infections cause inflammation and mucus production that can block the narrow eustachian tubes.
Allergies
Seasonal allergies, hay fever, and persistent rhinitis can cause chronic inflammation and excess mucus production, leading to prolonged eustachian tube dysfunction. Allergic reactions can keep the tubes swollen for extended periods.
Sinus Infections
Sinusitis can cause inflammation that extends to the eustachian tubes, blocking proper drainage and airflow. The increased mucus production associated with sinus infections compounds the problem.
Environmental Factors
Smoking damages the tiny hairs (cilia) that help clear mucus from the eustachian tubes. Exposure to secondhand smoke and air pollution can also contribute to tube dysfunction.
Effective Home Remedies for Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
Many cases of eustachian tube dysfunction can be managed effectively with simple home remedies. These treatments focus on reducing inflammation, promoting drainage, and equalizing pressure.
The Valsalva Maneuver
This technique involves gently forcing air through the eustachian tubes to equalize pressure. To perform the Valsalva maneuver:
- Take a deep breath
- Pinch your nostrils closed
- Gently blow air as if blowing your nose
- You should feel your ears “pop” as pressure equalizes
- Repeat 2-3 times as needed
Caution: Perform this maneuver gently to avoid damaging your eardrums. Stop if you experience pain or dizziness.
Swallowing and Yawning Exercises
Natural actions like swallowing and yawning can help open the eustachian tubes. Try these techniques:
- Deliberate swallowing while pinching your nose
- Chewing gum to promote frequent swallowing
- Induced yawning by thinking about or watching others yawn
- Drinking water in small sips while holding your nose
Steam Inhalation
Inhaling warm, moist air helps reduce inflammation and thin mucus, making it easier to drain from the eustachian tubes:
- Fill a bowl with hot water
- Add a few drops of eucalyptus or peppermint oil (optional)
- Lean over the bowl and cover your head with a towel
- Inhale the steam for 10-15 minutes
- Repeat 2-3 times daily
Warm Compress Application
Applying heat to the affected ear can help reduce pain and promote drainage:
- Soak a clean cloth in warm water
- Wring out excess water
- Hold the warm compress against the affected ear for 15-20 minutes
- Repeat several times throughout the day
Nasal Saline Irrigation
Using a saline solution to flush the nasal passages can help reduce congestion and inflammation that contributes to eustachian tube dysfunction:
- Use a neti pot or saline rinse bottle
- Mix 1/4 teaspoon of salt with 8 ounces of warm, sterile water
- Gently rinse each nostril
- Allow solution to drain completely
- Use 1-2 times daily during symptoms
Over-the-Counter Treatments
Several over-the-counter medications can provide relief from eustachian tube dysfunction symptoms:
Decongestants
Oral decongestants like pseudoephedrine can help reduce swelling in the nasal passages and eustachian tubes. Nasal decongestant sprays provide more targeted relief but should not be used for more than 3-5 days to avoid rebound congestion.
Antihistamines
For ETD caused by allergies, antihistamines can be highly effective. Options include:
- Loratadine (Claritin)
- Cetirizine (Zyrtec)
- Diphenhydramine (Benadryl)
- Fexofenadine (Allegra)
Pain Relievers
Over-the-counter pain medications can help manage ear pain and reduce inflammation:
- Ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) – reduces both pain and inflammation
- Acetaminophen (Tylenol) – provides pain relief
- Naproxen (Aleve) – longer-lasting anti-inflammatory effects
Medical Treatments and Professional Interventions
When home remedies and over-the-counter treatments are insufficient, medical intervention may be necessary:
Prescription Medications
Healthcare providers may prescribe stronger medications for persistent eustachian tube dysfunction:
- Nasal corticosteroids: Reduce inflammation in the nasal passages and eustachian tubes
- Antibiotics: Prescribed if bacterial infection is suspected
- Prescription antihistamines: For severe allergic reactions
- Proton pump inhibitors: If acid reflux is contributing to symptoms
Surgical Procedures
For chronic or severe cases, surgical options may be considered:
Myringotomy and Tube Insertion
This procedure involves making a small incision in the eardrum and inserting a tiny tube to allow air flow and fluid drainage. It’s commonly performed in children with chronic ETD.
Balloon Eustachian Tuboplasty
A minimally invasive procedure where a small balloon is inserted into the eustachian tube and inflated to widen the passage. This newer technique has shown promising results for adults with chronic ETD.
Adenoidectomy
Removal of enlarged adenoids may be recommended, especially in children, as swollen adenoids can block the eustachian tube openings.
Lifestyle Modifications and Prevention
Making certain lifestyle changes can help prevent eustachian tube dysfunction and reduce the frequency of episodes:
Allergy Management
- Identify and avoid known allergens
- Use air purifiers in your home
- Keep windows closed during high pollen seasons
- Wash bedding in hot water weekly
- Consider allergy testing and immunotherapy
Smoking Cessation
Quitting smoking is one of the most important steps for preventing chronic eustachian tube dysfunction. Smoking cessation programs, nicotine replacement therapy, and prescription medications can help.
Hygiene Practices
- Wash hands frequently to prevent respiratory infections
- Avoid touching your face, especially during cold and flu season
- Get annual flu vaccinations
- Maintain good overall health through proper nutrition and exercise
Managing ETD During Air Travel
Air travel can be particularly challenging for people prone to eustachian tube dysfunction. Here are strategies to minimize problems:
Before Flying
- Use a nasal decongestant 30 minutes before takeoff
- Consider postponing travel if you have an active cold or sinus infection
- Stay well-hydrated
During Flight
- Chew gum or suck on candy during takeoff and landing
- Perform the Valsalva maneuver gently during altitude changes
- Stay awake during takeoff and landing to actively equalize pressure
- Use specialized earplugs designed for air travel
When to Seek Medical Attention
While many cases of eustachian tube dysfunction resolve on their own, certain situations require professional medical evaluation:
- Severe or constant ear pain: ETD typically causes mild, intermittent pain
- Fever: May indicate a secondary infection requiring antibiotic treatment
- Hearing loss that doesn’t improve: Persistent hearing problems need evaluation
- Discharge from the ear: Could indicate eardrum perforation or infection
- Symptoms lasting more than 2-3 weeks: Chronic ETD may require specialized treatment
- Severe dizziness or balance problems: May indicate inner ear involvement
Comparing Treatment Effectiveness
| Treatment Type | Effectiveness | Time to Relief | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Valsalva Maneuver | Moderate | Immediate | Mild, recent-onset ETD |
| Steam Inhalation | Good | 30 minutes – 2 hours | Congestion-related ETD |
| Decongestants | Good | 1-4 hours | Cold or allergy-related ETD |
| Nasal Corticosteroids | Very Good | 1-3 days | Chronic or allergy-related ETD |
| Surgical Intervention | Excellent | 2-6 weeks | Chronic, treatment-resistant ETD |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: How long does eustachian tube dysfunction typically last?
A: Most cases of ETD resolve within 1-2 weeks, especially when related to a cold or upper respiratory infection. However, chronic cases can persist for months and may require medical treatment.
Q: Can children use the same remedies as adults?
A: Many remedies are safe for children, but dosages and techniques may need modification. Steam inhalation and warm compresses are generally safe, while medications should be used according to pediatric guidelines. Always consult a pediatrician for children’s ear problems.
Q: Is eustachian tube dysfunction dangerous?
A: ETD itself is usually not dangerous, but complications can develop if left untreated. These may include middle ear infections, hearing loss, or eardrum damage. Chronic cases should be evaluated by a healthcare provider.
Q: Can stress worsen eustachian tube dysfunction?
A: While stress doesn’t directly cause ETD, it can weaken your immune system and make you more susceptible to the respiratory infections that commonly trigger eustachian tube problems.
Q: Are there any foods that can help with ETD?
A: Foods with anti-inflammatory properties, such as those rich in omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin C, and antioxidants, may help reduce inflammation. Staying well-hydrated also helps thin mucus secretions. Avoid dairy if you notice it increases mucus production.
Understanding and implementing appropriate remedies for eustachian tube dysfunction can significantly improve your quality of life and prevent complications. Start with simple home remedies and gradually progress to medical treatments if symptoms persist or worsen. Remember that prevention through good hygiene, allergy management, and lifestyle modifications is often the best approach to managing this common but bothersome condition.
References
- https://familydoctor.org/condition/eustachian-tube-dysfunction/
- https://patient.info/ears-nose-throat-mouth/earache-ear-pain/eustachian-tube-dysfunction
- https://www.ent-sd.com/ent-medical-treatments-san-diego/ears-hearing/eustachian-tube-dysfunction/
- https://greenwichent.com/services/ear-nose-throat-care/ear/eustachian-tube-dysfunction/
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/22527-eustachian-tube-dysfunction
- https://www.brighamandwomens.org/surgery/otolaryngology/ear/eustachian-tube-dysfunction
- https://med.stanford.edu/ohns/OHNS-healthcare/earinstitute/conditions-we-treat/eustachian-tube-dysfunction.html
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK262265/
- https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamaotolaryngology/fullarticle/2825855
Read full bio of medha deb








