Eczema: Understanding the Skin Disorder
Navigating the complexities of eczema for clearer skin
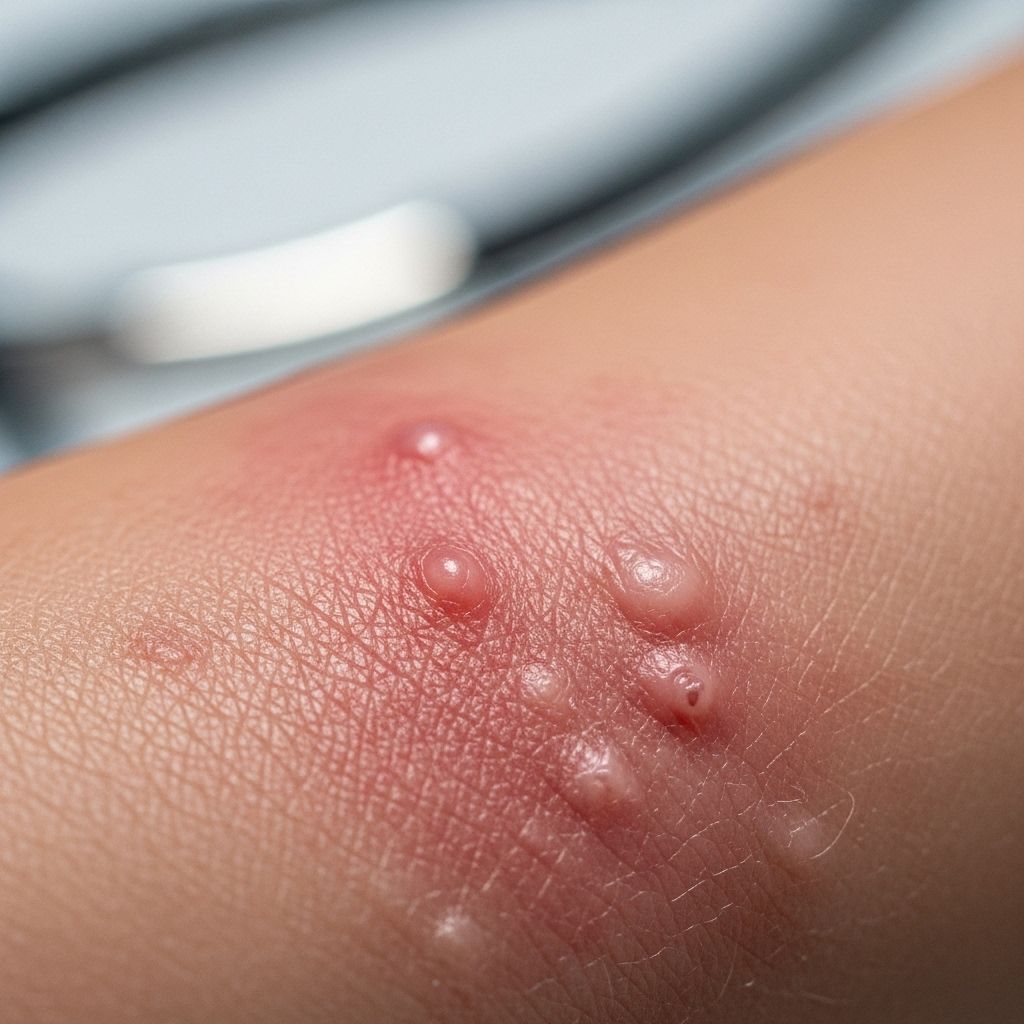
Introduction to Eczema
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a common skin condition characterized by dry, itchy, and inflamed skin. It is a chronic condition that can significantly impact one’s quality of life. Eczema affects people of all ages, but it often begins in childhood and can persist into adulthood.
Types of Eczema
There are several types of eczema, each with distinct symptoms and triggers. The most common types include:
- Atopic Dermatitis: This is the most common form, often beginning in childhood and linked to allergies and asthma.
- Contact Dermatitis: This type is caused by exposure to allergens or irritants, leading to redness and inflammation.
- Seborrheic Dermatitis: Typically affects oily areas of the body, causing scaly patches and redness.
Symptoms of Eczema
The primary symptoms of eczema include itchy skin, dryness, redness, and inflammation. In severe cases, the skin may crack, leading to further complications like infections.
Managing Eczema Symptoms
Effective management of eczema involves a combination of lifestyle changes and medical treatments:
- Moisturizing: Keeping the skin hydrated is crucial to prevent dryness and reduce itchiness.
- Topical Corticosteroids: These creams and ointments help reduce inflammation and can be prescribed by a doctor.
- Phototherapy: Involves exposure to specific wavelengths of light, which can be beneficial for severe cases unresponsive to other treatments.
- Biologics: Injectable medications like dupilumab that target specific proteins involved in inflammation.
Treatments for Eczema
Prescription and Over-the-Counter Options
For managing eczema, both prescription and over-the-counter treatments are available:
- Hydrocortisone Creams: Available over-the-counter for mild cases.
- Topical Immunomodulators (TIMs): Prescription creams like Elidel and Protopic for moderate to severe cases.
- Biologics: Injectables like dupilumab for severe eczema.
- Phototherapy: A treatment involving ultraviolet light exposure.
Complementary and Alternative Therapies
In addition to medical treatments, several complementary therapies can help manage eczema symptoms:
- Colloidal Oatmeal Baths: Soothe itchy skin.
- Wet-Wrap Therapy: Useful for severe cases.
- Stress Management Techniques: Meditation and acupuncture can reduce stress, which often exacerbates eczema.
Lifestyle Changes to Manage Eczema
Adopting certain lifestyle habits can significantly help in managing eczema:
- Moisturize Regularly: Use emollients to keep the skin hydrated.
- Avoid Triggers: Identify and avoid common triggers like harsh soaps, cold weather, or stress.
- Dress Comfortably: Wear soft, non-irritating clothing.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to maintain skin health.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Is there a cure for eczema?
Currently, there is no cure for eczema, but effective treatments can manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
Q: What are common triggers for eczema?
Common triggers include stress, certain foods, environmental factors like cold weather, and exposure to allergens or irritants.
Q: How can I prevent eczema flare-ups?
Preventing flare-ups involves maintaining a regular moisturizing routine, avoiding triggers, and using protective clothing.
References
- https://www.webmd.com/skin-problems-and-treatments/eczema/atopic-dermatitis-eczema
- https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/atopic-eczema/
- https://www.pfizer.com/disease-and-conditions/eczema
- https://nationaleczema.org/eczema/
- https://www.aaaai.org/tools-for-the-public/conditions-library/allergies/eczema-(atopic-dermatitis)-overview
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/9998-eczema
- https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/2020/0515/p590.html
Read full bio of medha deb












